1. Introduction: Understanding GNE Myopathy
GNE myopathy (GNEM) is a rare neuromuscular disorder caused by mutations in the GNE gene. The condition leads to progressive muscle atrophy, primarily affecting the lower limbs before spreading to other muscles.
Due to underdiagnosis, prevalence estimates have ranged from **1 to 9 cases per million**. However, these figures are likely **underestimations**, requiring a more accurate analysis based on **genetic data**.
2. Research Methodology: Using Genetic Databases
- Data Sources: The study analyzed allele frequencies from **large genetic databases** like gnomAD.
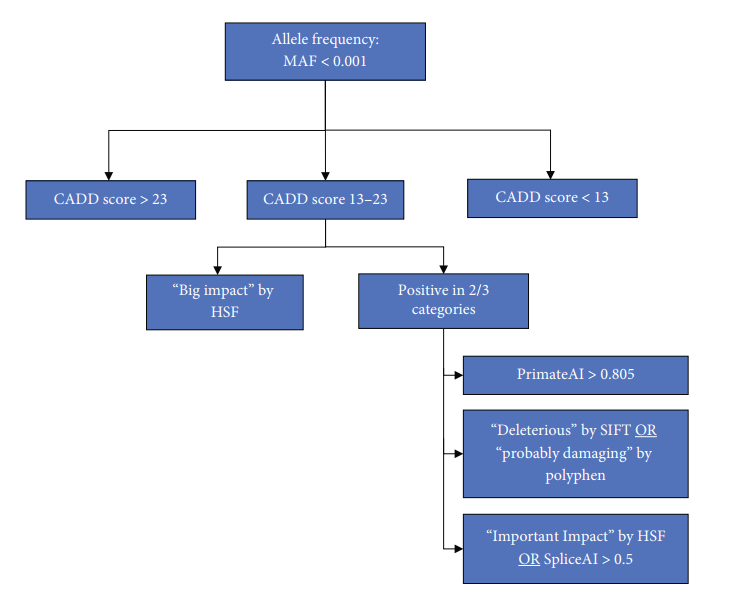
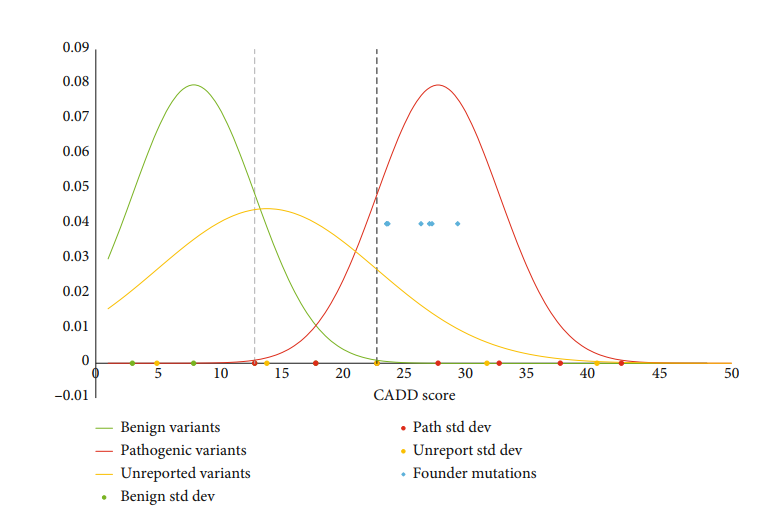
- Computational Analysis: Researchers used bioinformatics tools to assess pathogenicity of GNE variants.
- Prevalence Calculation: Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium models were applied to estimate GNEM occurrence across populations.
3. Key Findings: Higher Prevalence than Expected
The study estimated **GNEM prevalence** between:
- 11 to 87 cases per million (depending on variant severity).
- Significant variations across ethnic groups:
- Higher prevalence in **South Asians** and **East Asians**.
- Lower prevalence in **European populations**.
- Potential for embryonic lethality in certain severe variant combinations.
4. Implications for Healthcare and Diagnosis
These findings indicate that **GNEM is more widespread** than previously assumed. The study highlights:
- Need for better genetic screening to improve **early diagnosis**.
- Importance of precise prevalence data for allocating healthcare resources.
- Potential impact on clinical trial designs for GNEM treatments.
5. Conclusion: Improving GNEM Awareness and Detection
The study underscores the **need for more comprehensive genetic testing** to uncover **undiagnosed GNEM cases**. **Advancements in genetic sequencing** could bridge the gap between estimated and actual cases, leading to better patient care.
By refining **prevalence estimates**, researchers can help improve **clinical awareness**, accelerate **therapeutic development**, and enhance **resource allocation** for GNEM patients.





| Published | 7/17/2024 |
| Address | https://doi.org/10.1155/2024/7377504 |
| Authors | Alexa Derksen ,1,2 Rachel Thompson ,2 Madeeha Shaikh ,3 Sally Spendiff ,Theodore J. Perkins ,4,5 and Hanns Lochmüller 2,6,7,8,9 |