Background: Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe genetic disorder caused by mutations in the DMD gene. These mutations disrupt the dystrophin protein, essential for muscle function. Current treatments, like exon-skipping oligonucleotides, have limitations due to their short lifespan and need for frequent administration.
Objective: This study explored the use of a self-complementary adeno-associated virus (scAAV9) vector expressing U7 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) to target exon 2 of the DMD gene. This approach aims to restore dystrophin expression by inducing exon skipping.
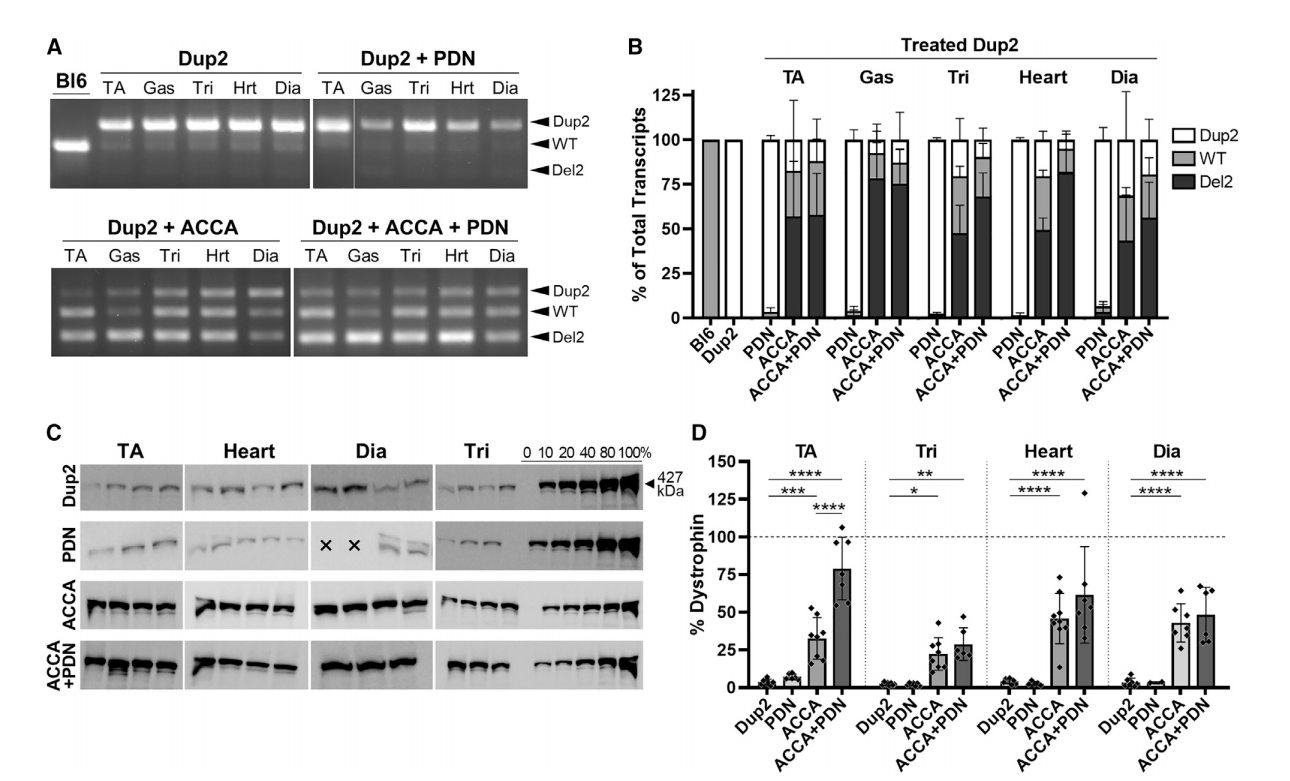
Methods: The vector was tested in a Dup2 mouse model, which carries a duplication of exon 2. Two strategies were assessed: one-time systemic injection at neonatal or adult stages, and co-treatment with prednisolone. Efficacy was evaluated using RT-PCR, Western blot, immunofluorescence, and histopathological assessments.
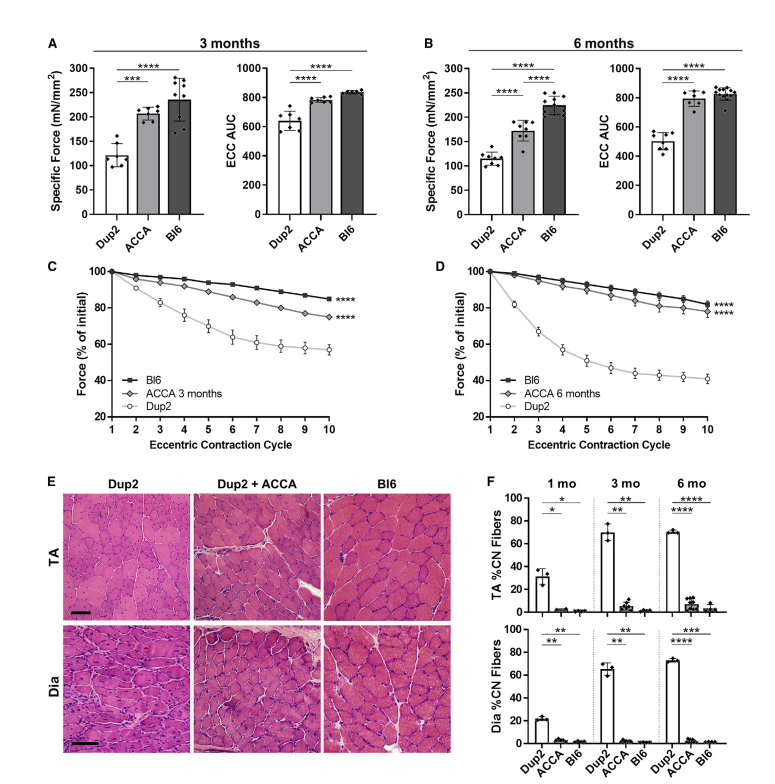
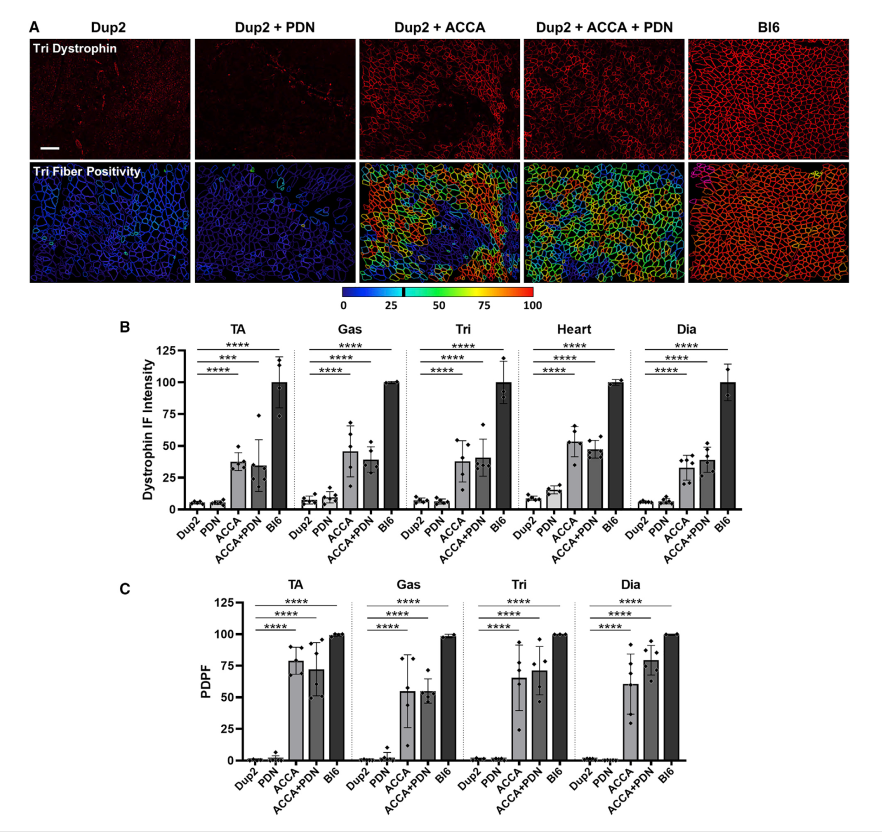
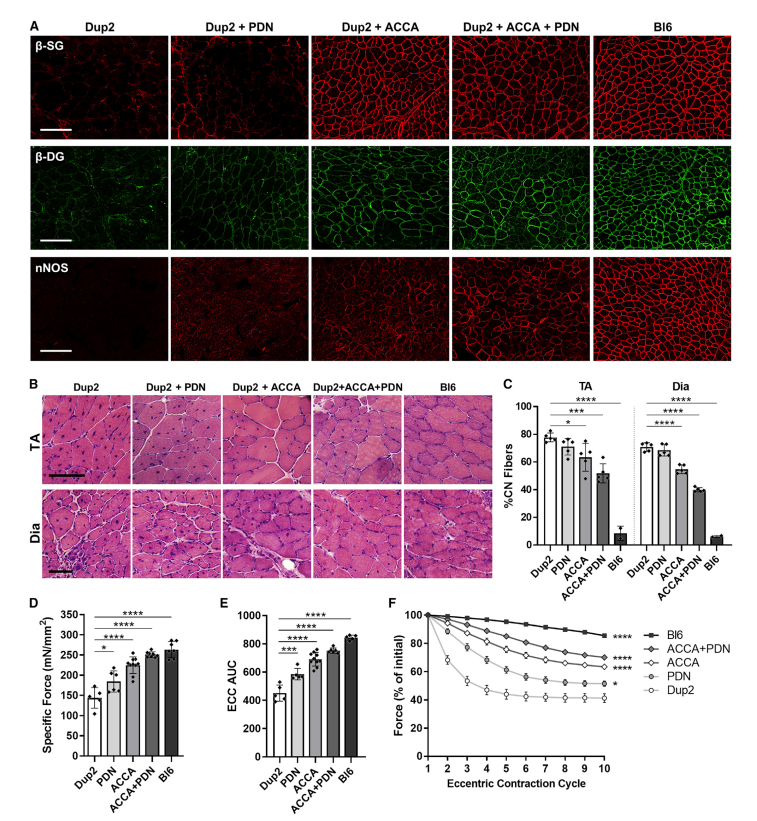
Findings (Adults): Injection in 2-month-old mice resulted in 69-95% exon skipping and significant dystrophin restoration. Immunofluorescence showed 33-53% intensity and up to 79% positive fibers, improving muscle structure and function.
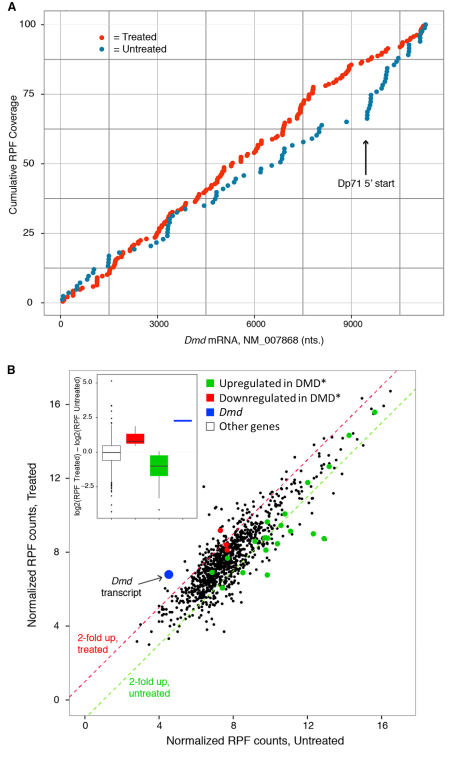
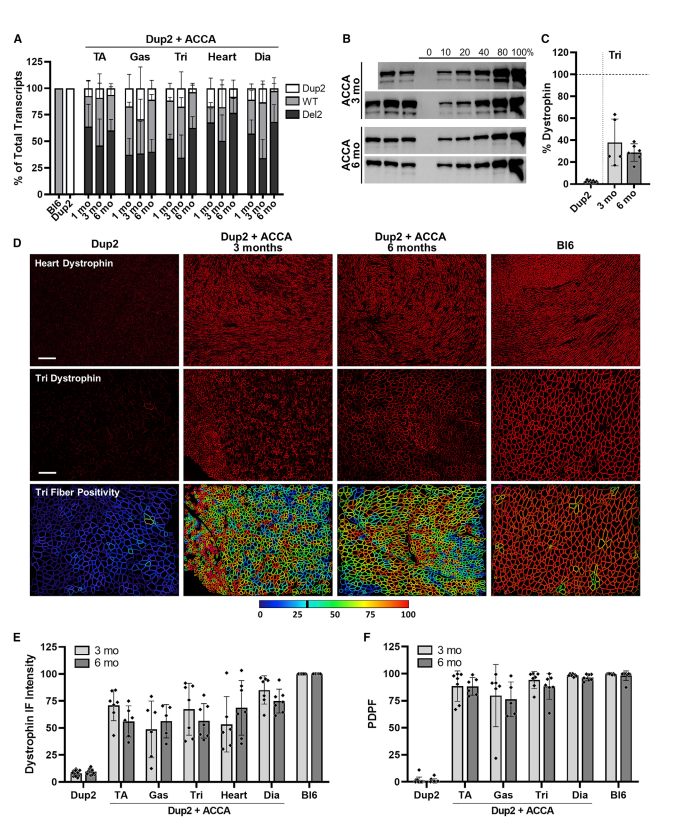
Findings (Neonates): Neonatal injection achieved up to 99% dystrophin-positive fibers and near-complete disease correction over six months. Benefits included persistent exon skipping and robust dystrophin production without significant off-target effects.
Conclusions: The results demonstrate that scAAV9.U7snRNA.ACCA provides durable, robust dystrophin restoration, supporting its potential as a clinical therapy for DMD, especially for exon 2 duplications.
زمینه: دیستروفی عضلانی دوشن (DMD) یک اختلال ژنتیکی شدید است که به علت جهشهای ژن DMD ایجاد میشود. این جهشها پروتئین دیستروفین را که برای عملکرد عضلات ضروری است، مختل میکنند. درمانهای فعلی، مانند الیگونوکلئوتیدهای حذف اگزون، به دلیل عمر کوتاه و نیاز به تزریق مکرر محدودیت دارند.
هدف: این مطالعه استفاده از وکتور ویروس مرتبط با آدنو (scAAV9) را که RNA کوچک هستهای U7 (snRNA) را بیان میکند، بررسی کرد تا اگزون 2 ژن DMD را هدف قرار دهد و تولید دیستروفین را بازیابی کند.
روشها: این وکتور در مدل موشی Dup2 با تکثیر اگزون 2 آزمایش شد. دو استراتژی ارزیابی شد: تزریق سیستمیک یکبار در مراحل نوزادی یا بالغ، و درمان همزمان با پردنیزولون. اثربخشی با استفاده از RT-PCR، وسترن بلات، ایمنوفلورسانس و ارزیابیهای بافتشناسی ارزیابی شد.
یافتهها (بالغین): تزریق در موشهای دو ماهه 69-95٪ حذف اگزون و بازسازی قابلتوجه دیستروفین را به دنبال داشت. ایمنوفلورسانس نشان داد 33-53٪ شدت و تا 79٪ فیبرهای مثبت، ساختار و عملکرد عضلات را بهبود داده است.
یافتهها (نوزادان): تزریق در نوزادان تا 99٪ فیبرهای مثبت دیستروفین و اصلاح تقریباً کامل بیماری طی شش ماه را به دست آورد. مزایا شامل حذف مداوم اگزون و تولید قوی دیستروفین بدون اثرات جانبی قابل توجه بود.
نتیجهگیری: نتایج نشان میدهد که scAAV9.U7snRNA.ACCA بازسازی پایدار و قوی دیستروفین را فراهم میکند و پتانسیل درمانی آن را برای DMD، به ویژه برای تکثیر اگزون 2 تأیید میکند.









| Field | Details |
| Authors | Nicolas Wein, Tatyana A. Vetter, Adeline Vulin, Tabatha R. Simmons, Emma C. Frair, Adrienne J. Bradley, Liubov V. Gushchina, Camila F. Almeida, Nianyuan Huang, Daniel Lesman, Dhanarajan Rajakumar, Robert B. Weiss, Kevin M. Flanigan |
| Corresponding Authors | Nicolas Wein (nicolas.wein@nationwidechildrens.org), Kevin M. Flanigan (kevin.flanigan@nationwidechildrens.org) |
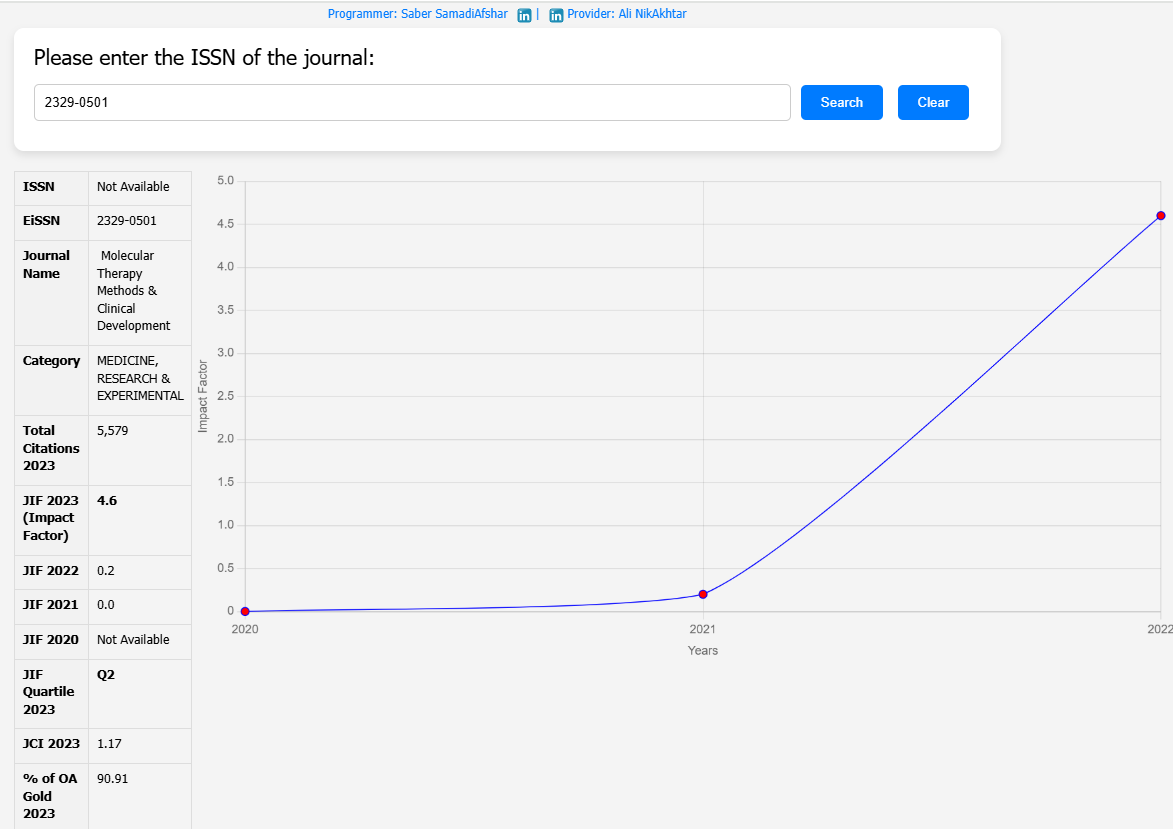
| Article Title | Systemic delivery of an AAV9 exon-skipping vector significantly improves or prevents features of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in the Dup2 mouse |
| Publication Date | 1-Sep-22 |
| Journal Name | Molecular Therapy: Methods & Clinical Development |
| Keywords (English) | #DuchenneMuscularDystrophy #DMD #GeneTherapy #ExonSkipping #AAV9 #U7snRNA #DystrophinRestoration #Dup2MouseModel |
| Methods Used | Gene therapy, RT-PCR, Western blot, Immunofluorescence, Histopathology, qPCR, Ribosome Profiling, RNA sequencing |
| DOI | 10.1016/j.omtm.2022.07.005 |