more
Anti-dystrophin Antibodies and Their Applications in Western Blotting for Quantifying Dystrophin Rescue
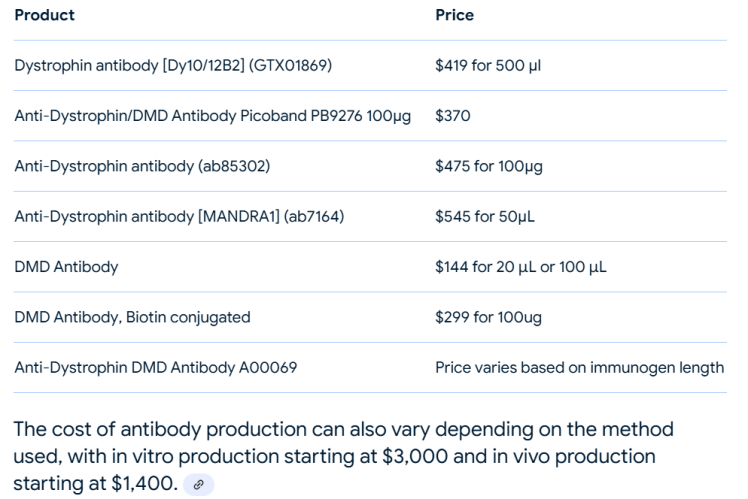
Dystrophin, a crucial protein for maintaining muscle integrity, is severely deficient in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) patients. Quantifying dystrophin restoration following therapeutic interventions is essential for evaluating treatment efficacy. Western blotting, a widely used protein analysis technique, plays a pivotal role in this quantification, with anti-dystrophin antibodies being central to its success. Anti-dystrophin antibodies are specifically designed to detect and bind dystrophin protein, making them indispensable for Western blot …