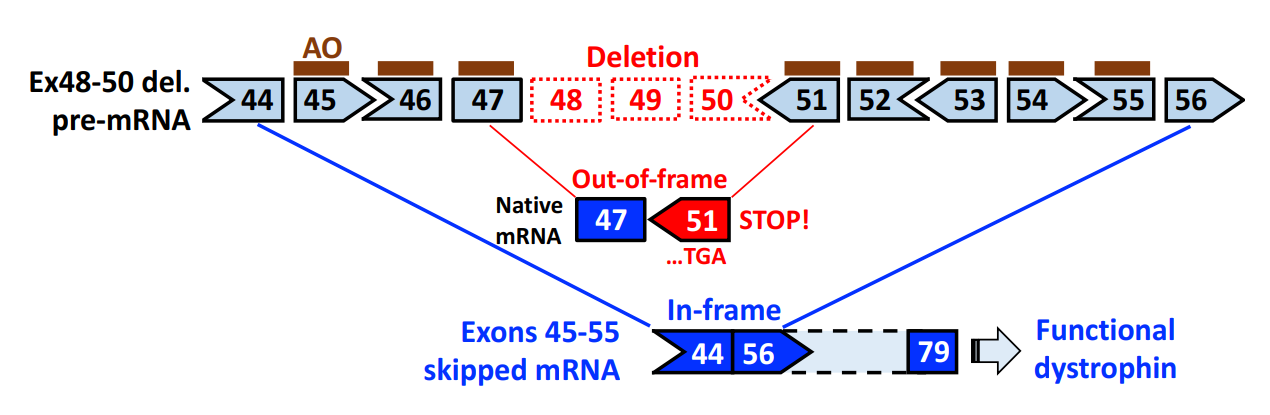
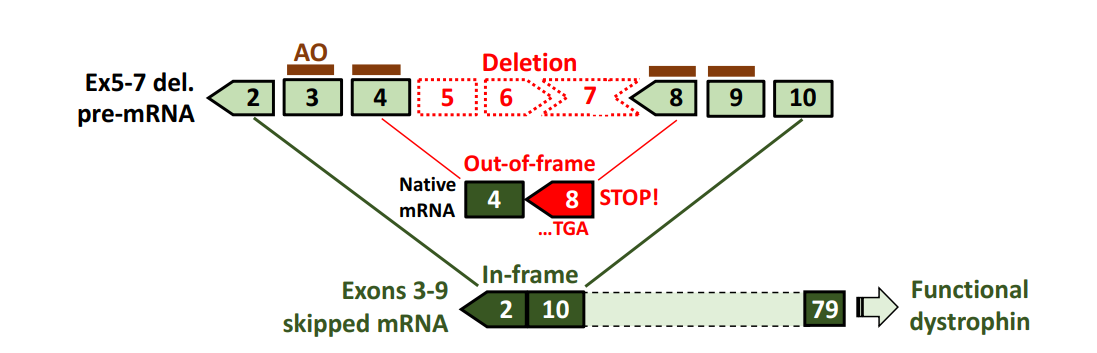
The paper explores an advanced therapeutic strategy for treating Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), a severe genetic disorder caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene. This mutation leads to the absence of functional dystrophin protein, which is essential for maintaining muscle integrity. One emerging treatment method involves antisense oligonucleotide (AO)-mediated exon skipping, where specific exons are skipped during gene expression to produce a functional, albeit shortened, version of the dystrophin protein. This strategy is particularly promising for patients with certain deletions in the DMD gene.
Key Exon Hot Spots in Dystrophin Gene
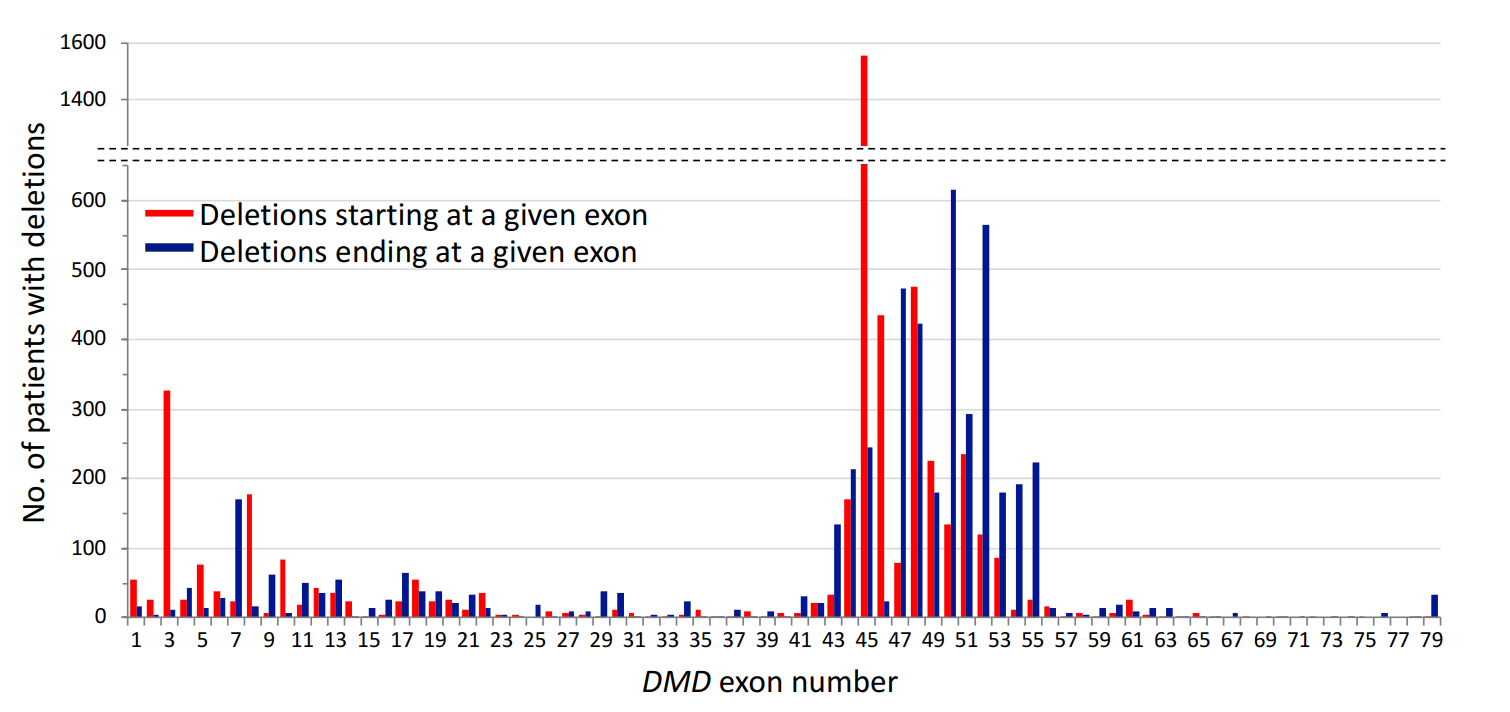
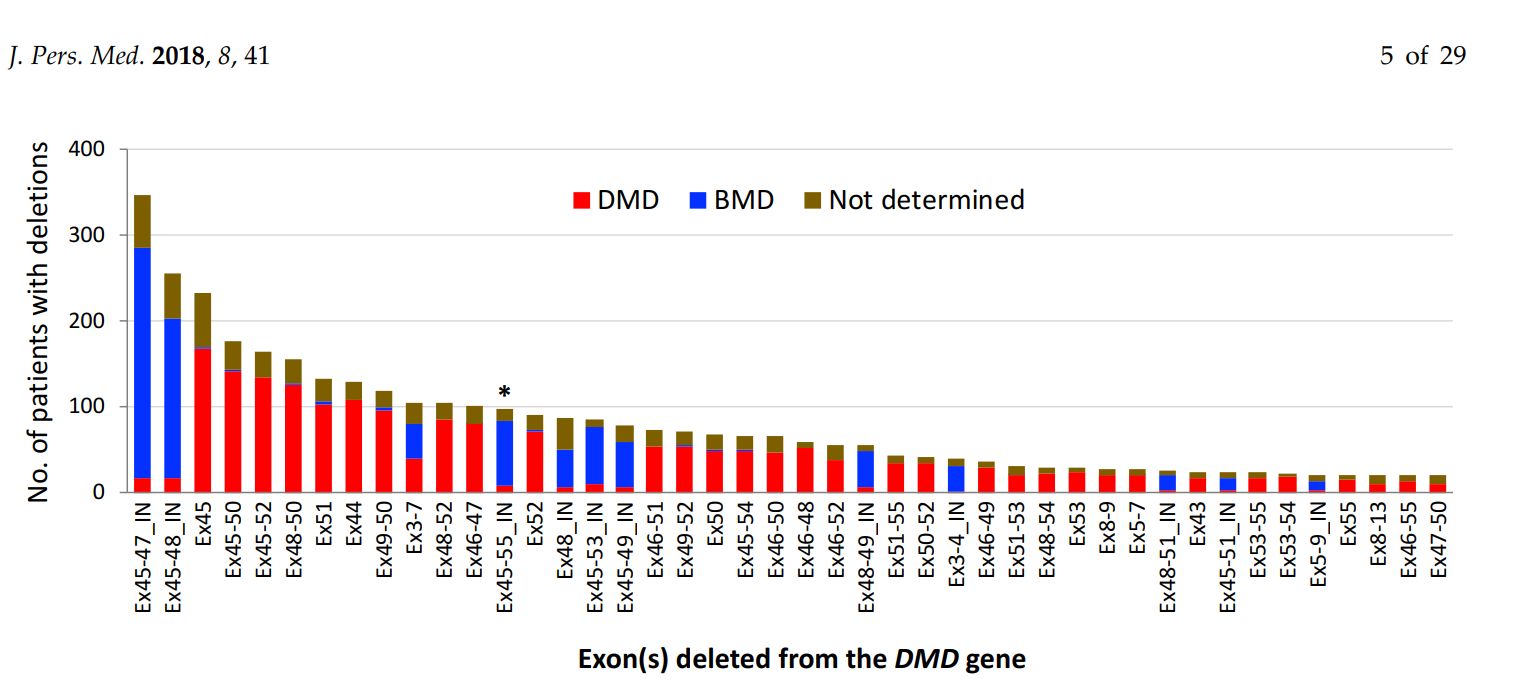
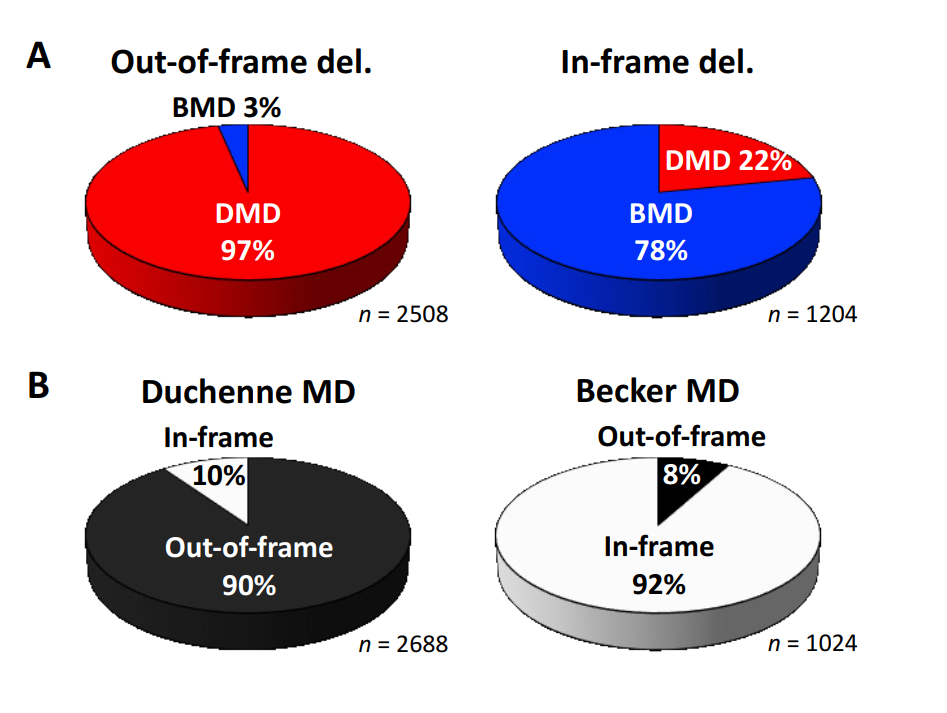
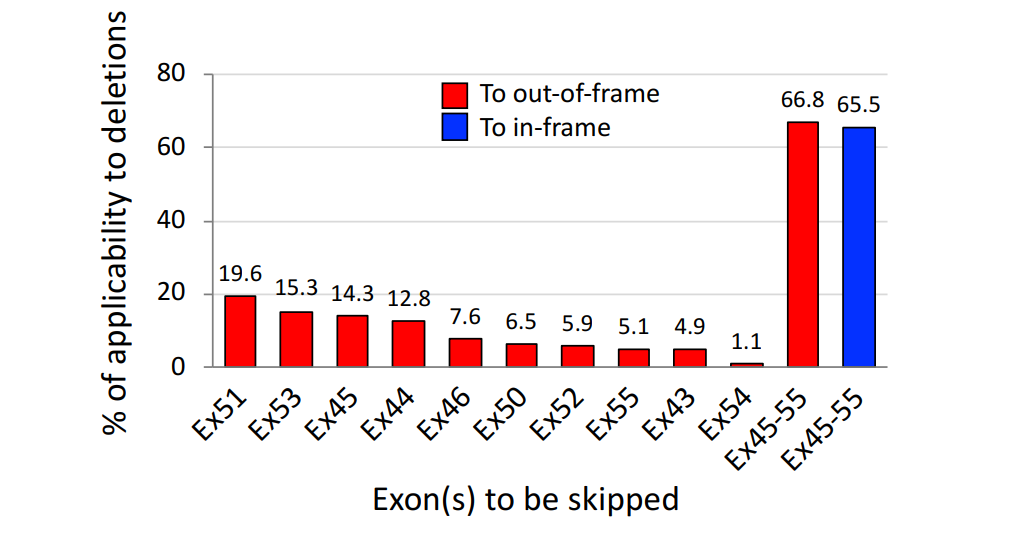
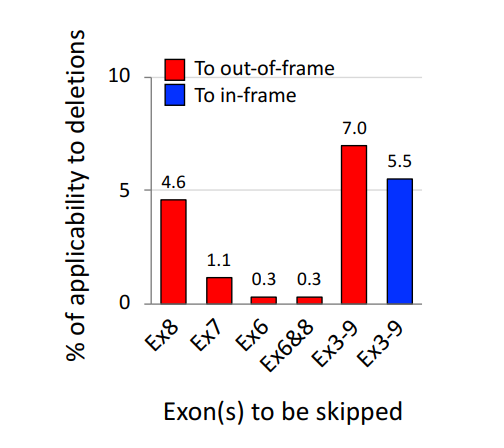
The authors emphasize the significance of multiple exon skipping, particularly targeting "hot spots" in the dystrophin gene, such as exons 45–55 and exons 3–9. This approach could expand treatment availability, benefiting not only patients with out-of-frame deletions (which cause severe DMD) but also those with certain in-frame deletions. The paper highlights preclinical success and provides a rationale for further research.
Challenges in Antisense Therapy
The study outlines various challenges, including the need for optimized antisense oligonucleotide design and efficient delivery methods. While PMOs (phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers) have shown promise, limited muscle tissue distribution and bioavailability remain major hurdles. Innovations like vivo-PMOs, which enhance cellular uptake, are discussed as potential solutions.
Conclusion and Future Directions
Multiple exon skipping holds great promise as a therapeutic option for DMD, potentially expanding treatment to a wider range of patients with different gene mutations. However, further research is necessary to refine the technique, improve drug delivery, and conduct clinical trials to confirm the efficacy observed in preclinical studies.



| Authors (whole) | Yusuke Echigoya, Kenji Rowel Q. Lim, Akinori Nakamura, Toshifumi Yokota |
| Corresponding Author | Yusuke Echigoya |
| Article Title | Multiple Exon Skipping in the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Hot Spots: Prospects and Challenges |
| Publication Date | 7-Dec-18 |
| Journal Name | Journal of Personalized Medicine (J. Pers. Med.) |
| Journal Ranking | N/A |
| Keywords | Dystrophinopathy, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD), antisense oligonucleotide, multiple exon skipping, PMO, vivo-PMO |
| Methods Used | Antisense oligonucleotide design, exon skipping, preclinical models, molecular diagnostic methods |
| DOI | 10.3390/jpm8040041 |














