more
Immortalized Skeletal Muscle Cells: Advancing DMD Research
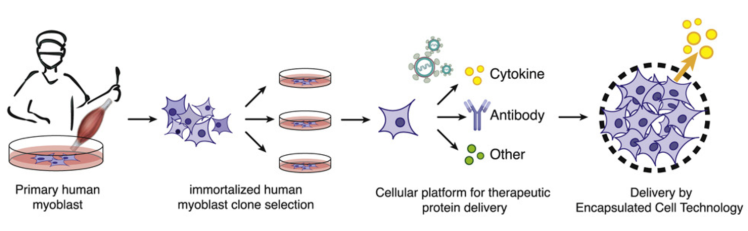
Immortalized Skeletal Muscle Cells: Advancing DMD Research Immortalized skeletal muscle cells derived from both healthy individuals and Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) patients offer a powerful platform for scientific discovery in the field of neuromuscular disorders. These cells provide a reproducible model for studying disease mechanisms and investigating therapeutic strategies, particularly in the context of exon-skipping therapies. By using these immortalized cells, researchers can explore how …