1. Introduction: Personalized ASO Therapies
This paper provides consensus guidelines for designing Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) tailored to individual patients, known as N-of-1 therapies. ASOs are short, synthetic DNA strands that modify gene expression by altering pre-mRNA splicing, offering treatment potential for various genetic diseases.
A successful example of this approach is Milasen, an ASO developed for a single patient with Batten disease, demonstrating the feasibility of personalized genetic medicine.
2. Key Recommendations for ASO Development
The guidelines emphasize three major principles for effective ASO design:
- Standardized Experimental Designs: Ensuring consistency in testing methodologies.
- Reference ASOs for Consistency: Using validated ASO sequences to compare results across studies.
- Data Sharing: Promoting open collaboration among researchers to advance the field of personalized therapies.
3. ASO Preclinical Evaluation: Essential Steps
Proper preclinical evaluation is critical for the success of N-of-1 ASOs. The following steps ensure high efficacy and minimal off-target effects:
- Design Multiple ASO Candidates: Testing several ASO sequences to identify the most effective one.
- In Vitro Cell Models: Using patient-derived cells to evaluate splicing correction and functional improvements.
- Testing in Relevant Models: Assessing ASO effects in disease-relevant animal models.
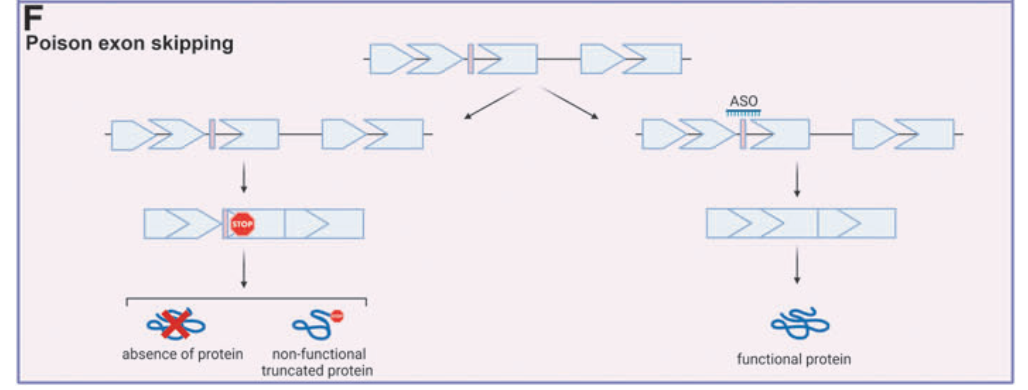
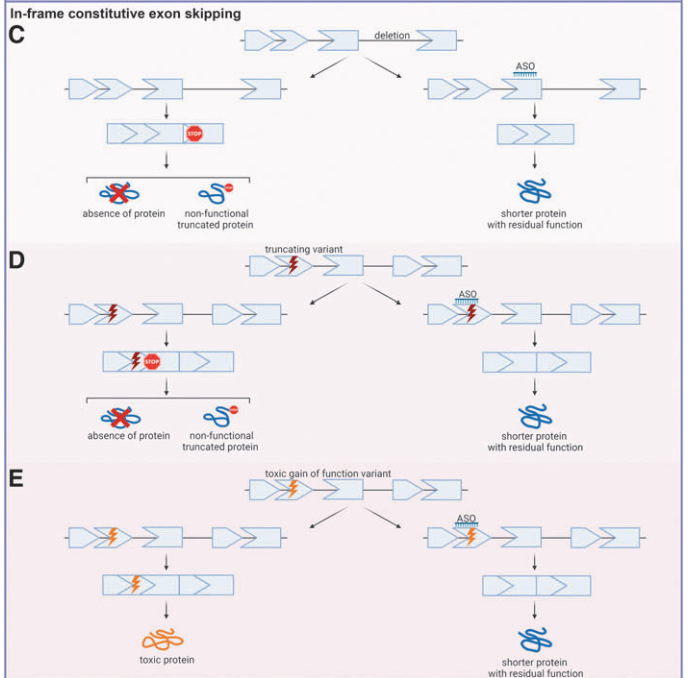
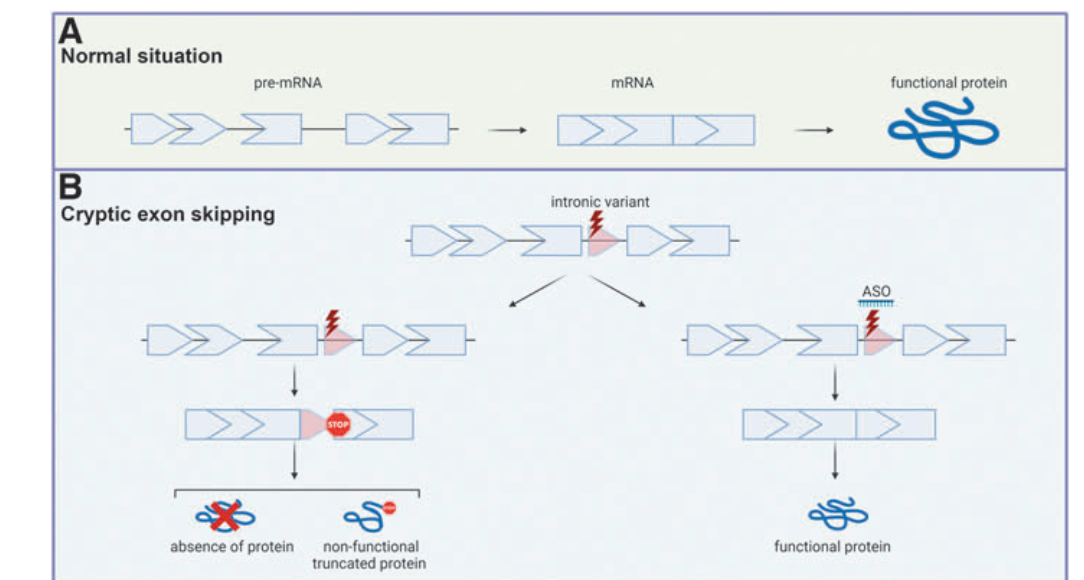
4. Types of Exon Skipping for ASO Therapy
Different exon-skipping strategies are used in ASO therapies:
- Targeting Cryptic Exons: Suppressing unintended exons that cause protein dysfunction.
- Modifying Constitutive Exons: Restoring proper splicing in genetic disorders like Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD).
- Blocking Poison Exons: Preventing premature protein truncation in diseases like Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA).
5. ASO Design Considerations
Effective ASO design depends on multiple factors:
- Nucleotide Composition: Optimizing chemical modifications to enhance stability.
- Target Selection: Choosing the most effective exon for therapeutic intervention.
- Minimizing Off-Target Effects: Conducting bioinformatics analyses to ensure specificity.
6. The Future of N-of-1 ASO Therapies
To advance personalized ASO therapies, collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and regulatory bodies is essential. The study highlights the need for:
- Global Data Sharing: Improving research efficiency by pooling genetic and clinical data.
- Standardized Guidelines: Establishing best practices for preclinical testing and regulatory approval.
- Regulatory Pathways: Accelerating the development of patient-specific therapies.
7. Conclusion
The guidelines presented in this paper serve as a foundation for improving ASO therapy development. By refining experimental designs, standardizing methodologies, and fostering collaborative research, the potential for N-of-1 ASO treatments to benefit patients with rare mutations is significantly enhanced.






| Published | Number 1, 2023 |
| Address | DOI: 10.1089/nat.2022.0060 |
| Authors | Annemieke Aartsma-Rus,1–3 Alejandro Garanto,1,4 Willeke van Roon-Mom,1,2 Erin M. McConnell,3 Victoria Suslovitch,3,5 Winston X. Yan,3 Jonathan K. Watts,6 and Timothy W. Yu, |














