1. Introduction
**Spinal and Bulbar Muscular Atrophy (SBMA)** is a rare **adult-onset neurodegenerative disorder** that affects **motor neurons and skeletal muscle**. It is caused by **trinucleotide (CAG) expansions** in the **androgen receptor (AR) gene**, leading to toxic polyglutamine (polyQ) protein accumulation. SBMA shares characteristics with **polyglutamine diseases** (e.g., Huntington’s disease) and **motor neuron disorders** (e.g., ALS), making it a **unique research focus** in the field of neuromuscular diseases.
2. Nucleic Acid-Based Therapies: A New Approach
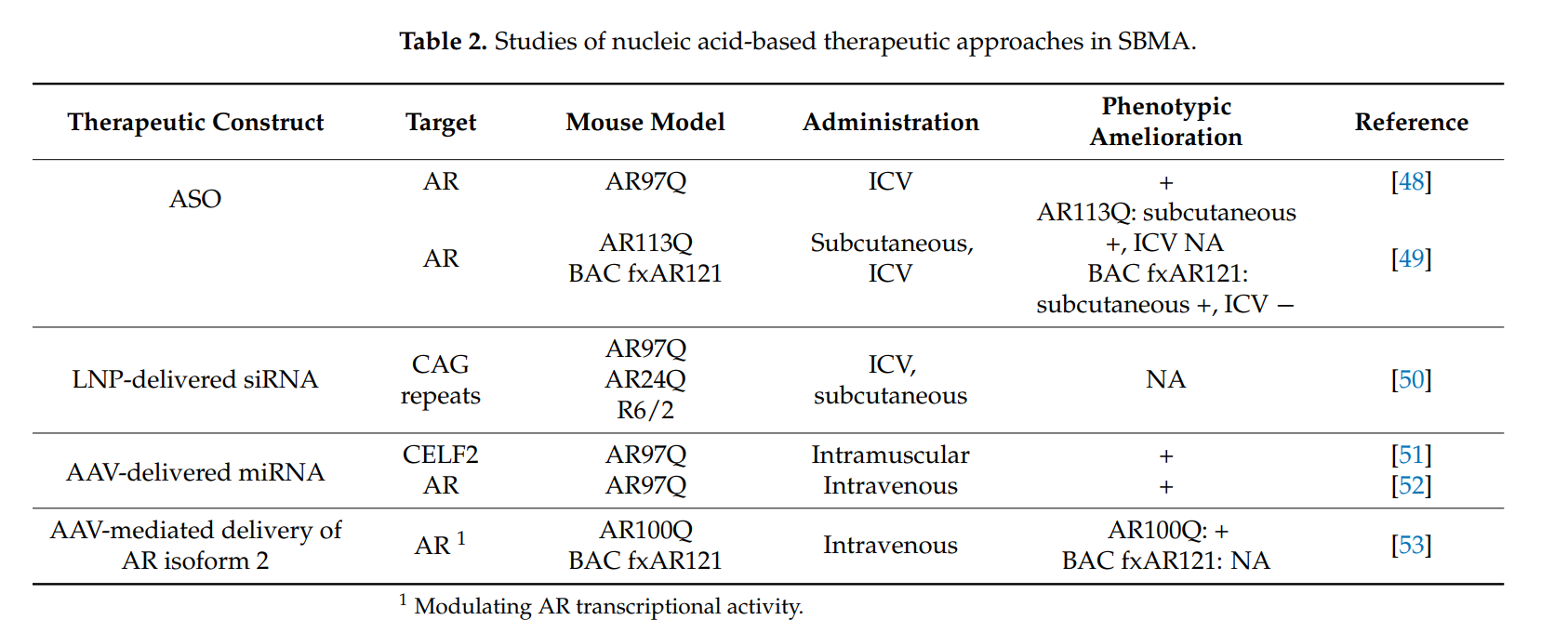
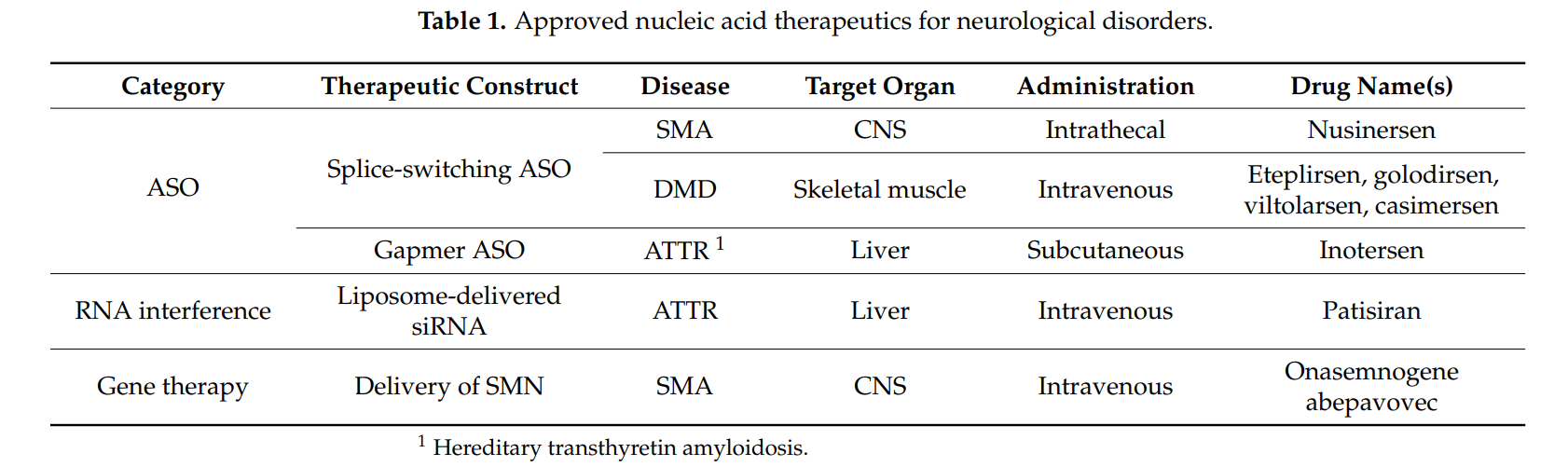
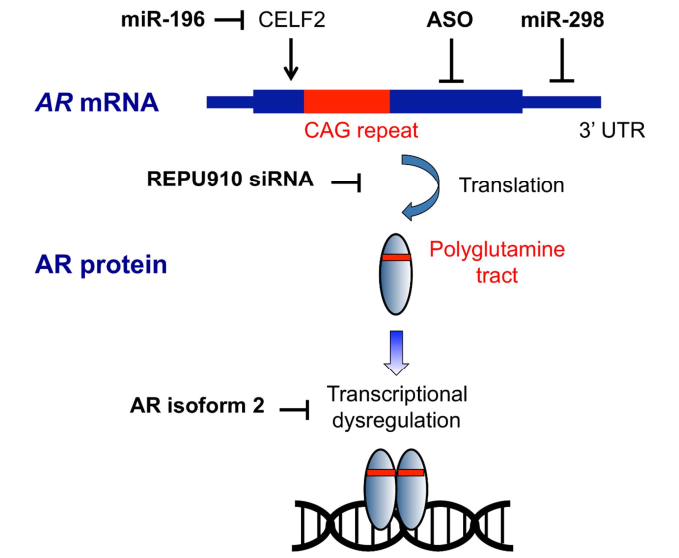
- Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs): These molecules selectively bind to **mutant AR mRNA** to block its translation and reduce **toxic protein accumulation**.
- Small Interfering RNAs (siRNAs): Target **CAG repeat expansions** to silence mutant gene expression.
- Gene Therapy: **AAV-based approaches** attempt to modify the **androgen receptor gene** to prevent polyQ toxicity.
3. Challenges in Treating SBMA
Despite promising results in **preclinical models**, **drug delivery to the CNS and skeletal muscle remains challenging**. Current therapies, such as **ASOs**, can reduce mutant **androgen receptor expression** in muscle, improving **strength and survival** in animal models. However, delivery to the **spinal cord and brainstem** is **limited** due to the **blood-brain barrier (BBB)**. Alternative **lipid nanoparticle-based siRNA** delivery methods are being explored to enhance treatment distribution.
4. Future Directions & Innovations
- **Developing better biomarkers** to track disease progression and **treatment efficacy**.
- **Enhancing drug delivery systems**, such as **brain-penetrant ASOs** and **long-acting oligonucleotides**.
- **Exploring CRISPR-based gene editing** to **permanently correct** the androgen receptor mutation.
- **Combining therapies** to **target both motor neurons and skeletal muscles**, preventing disease progression.
5. Conclusion
**Nucleic acid-based therapies** offer **great potential** for **treating SBMA**, but significant challenges in **drug delivery and long-term efficacy** must be addressed. Ongoing **clinical trials and technological advancements** will be crucial in making these therapies **more effective, accessible, and widely available** for SBMA patients.

| Published | 1/5/2022 |
| Address | https://doi.org/10.3390/ genes13010109 |
| Authors | Tomoki Hirunagi 1, Kentaro Sahashi 1, Katherine G. Meilleur 2 and Masahisa Katsuno 1,3,* |














