1. Introduction
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (**DMD**) is a severe **genetic disorder** caused by **mutations in the dystrophin gene**, leading to **progressive muscle deterioration**. The absence of **functional dystrophin** results in **muscle weakness**, cardiac and respiratory complications, and ultimately **premature mortality**. While **corticosteroids** can delay disease progression, they come with significant side effects. Recently, **gene therapy** and **antisense oligonucleotide (AON) therapy** have emerged as potential treatments, primarily targeting mutations in the **exon 43–55** region, leaving **mutations in exon 2–22 underserved**.
2. Gene Therapy: AAV-Based Approaches
- Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Vectors – Used for delivering **corrected dystrophin sequences**.
- Challenges: **Small vector capacity**, **immune system responses**, and **off-target effects**.
- Astellas Gene Therapies' scAAV9.U7.ACCA – Targeting **exon 2 duplication**, showing **promising preclinical results**.
3. Antisense Oligonucleotide (AON) Therapy
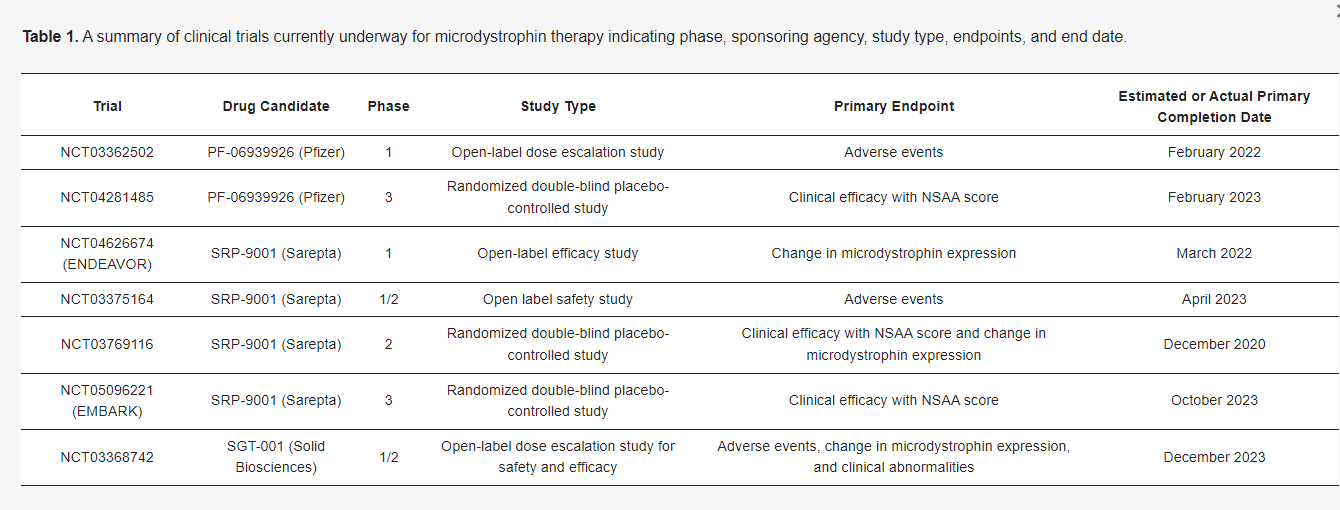
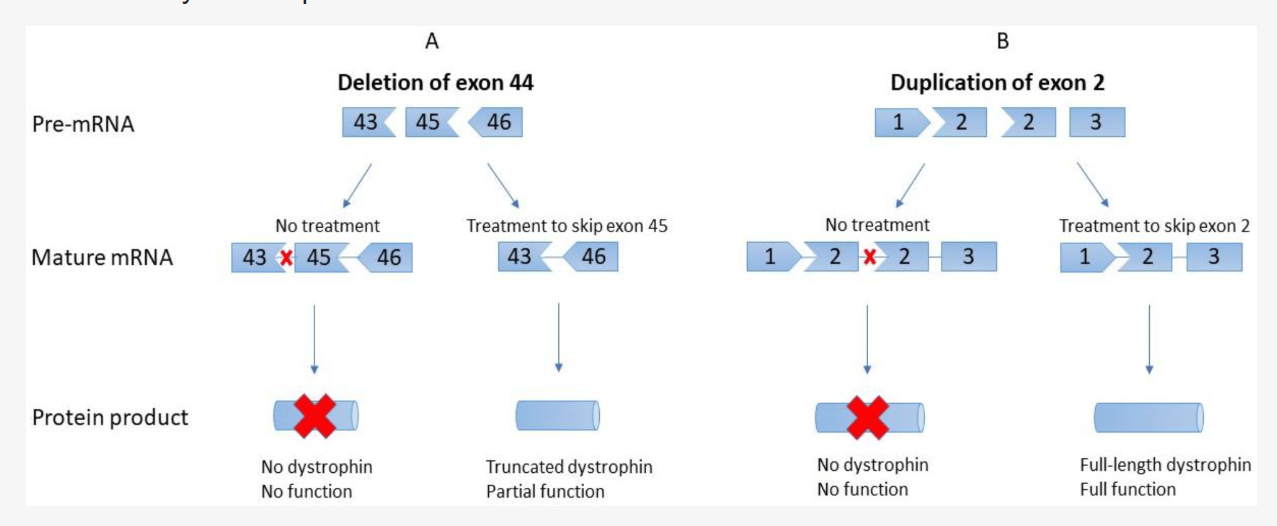
**AONs** function by directing the splicing machinery to **skip mutated exons**, restoring the **reading frame** of the dystrophin gene. While FDA-approved **AON therapies exist for exon 51, 53, and 45**, **no treatments currently exist for exon 2–22 mutations**. **Exon skipping for exons 3–9** has shown promise in preclinical studies, potentially converting severe **DMD phenotypes into milder BMD-like conditions**.
4. Microdystrophin Therapy: A Novel Gene Therapy Approach
- Concept: Uses **AAV vectors** to deliver **truncated but functional dystrophin**.
- Advantages: Can **bypass large mutations** and improve **muscle stability**.
- Challenges: Limited **AAV vector capacity**, potential **immune reactions**, and **high cost**.
5. Future Directions & Challenges
- **Expanding therapy to exon 2–22 mutations** – Currently underserved in clinical trials.
- **Improving delivery methods** – Enhancing **AON efficiency** and **AAV targeting precision**.
- **Addressing immune responses** – Developing **immune suppression strategies** for gene therapy.
- **Reducing treatment costs** – Increasing accessibility for **more DMD patients worldwide**.
6. Conclusion
While **gene therapy and exon skipping** offer **hope for DMD patients**, **significant challenges** remain in expanding these therapies to **exon 2–22 mutations**. Ongoing **clinical trials** and **technological advancements** will be crucial in developing **effective, safe, and widely accessible treatments** for all DMD patients.


| Published | 1/28/2022 |
| Address | https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13020257 |
| Authors | Harry Wilton-Clark and Toshifumi Yokota |














