1. Introduction
This study explores how knocking down the **circular RNA CDR1as** affects **goat skeletal muscle satellite cells (SMSCs)**. Researchers investigated its interaction with **miR-27a-3p** and **ANGPT1** during **muscle differentiation**, providing insights into **muscle growth regulation**.
2. Key Findings
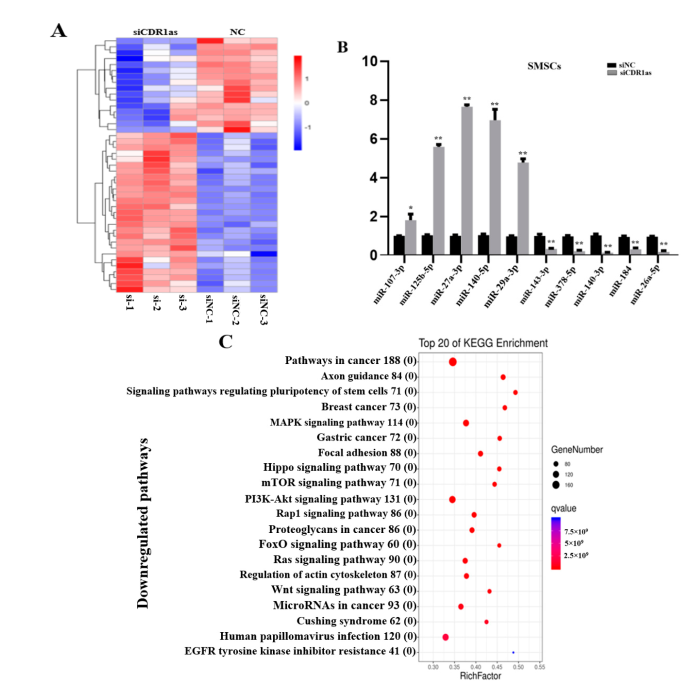
- CDR1as **knockdown upregulates** **miR-27a-3p**, which **inhibits ANGPT1**.
- This downregulation **reduces muscle satellite cell differentiation**.
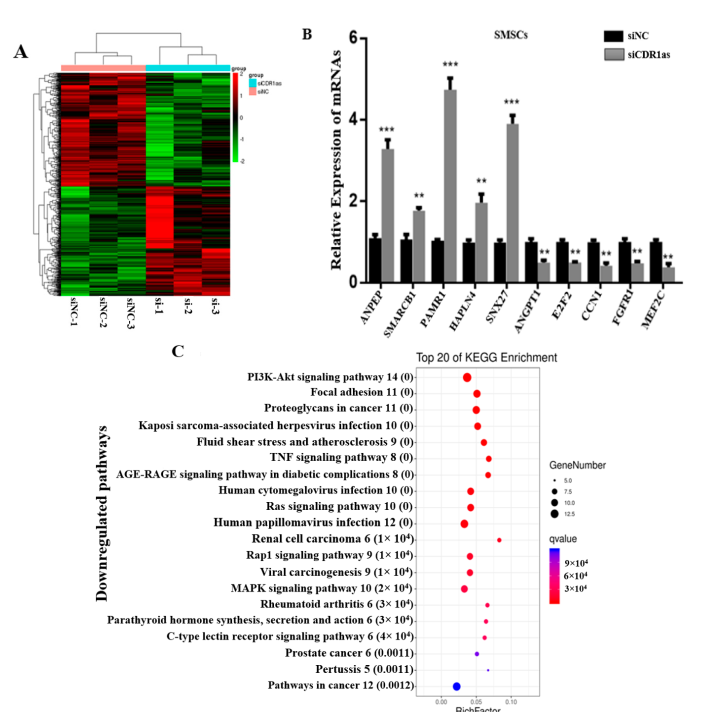
- RNA sequencing revealed **43 miRNAs** and **789 mRNAs** with altered expression.
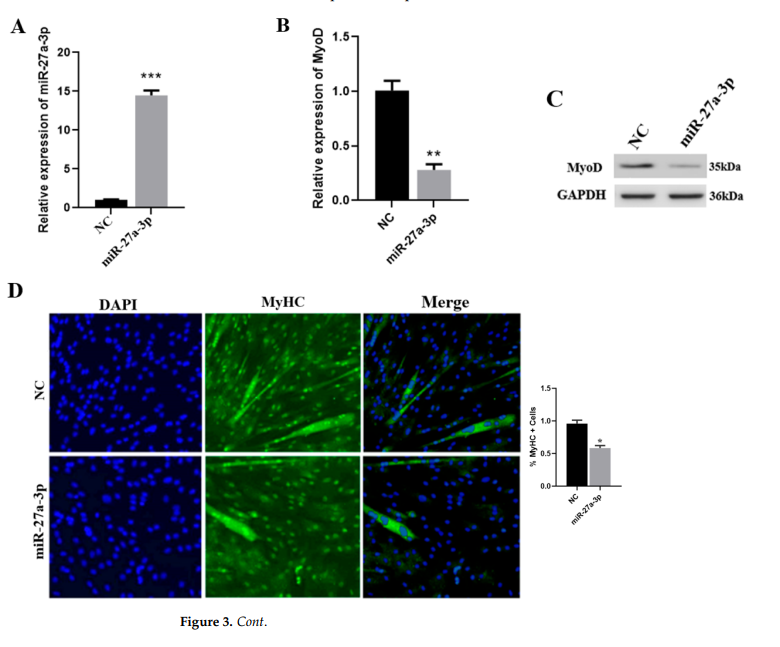
- miR-27a-3p negatively affects **MyoD**, a key muscle differentiation marker.
3. Mechanism: The CDR1as-miR-27a-3p-ANGPT1 Regulatory Network
The study suggests that **CDR1as acts as a sponge** for **miR-27a-3p**, preventing it from **downregulating ANGPT1**. When **CDR1as is knocked down**, **miR-27a-3p is upregulated**, leading to **ANGPT1 suppression** and **reduced differentiation of muscle satellite cells**.
4. Implications for Muscle Growth and Development
- Targeting **CDR1as-miR-27a-3p-ANGPT1** could help **regulate muscle growth**.
- Potential applications in **livestock improvement** and **muscle-related diseases**.
- Further research is needed to **validate therapeutic approaches**.
5. Conclusion
This study uncovers a **new regulatory pathway** influencing muscle differentiation. **CDR1as knockdown increases miR-27a-3p**, suppressing **ANGPT1** and **hindering muscle growth**. These findings pave the way for future **gene-targeting strategies** in **muscle biology**.



| Published | 4/9/2022 |
| Address | https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040663 |
| Authors | Bismark Kyei , Emmanuel Odame, Li Li , Liu Yang, Siyuan Zhan, Juntao Li, Yuan Chen, Dinghui Dai, Jiaxue Cao, Jiazhong Guo, Tao Zhong , Linjie Wang and Hongping Zhang |














