1. Introduction
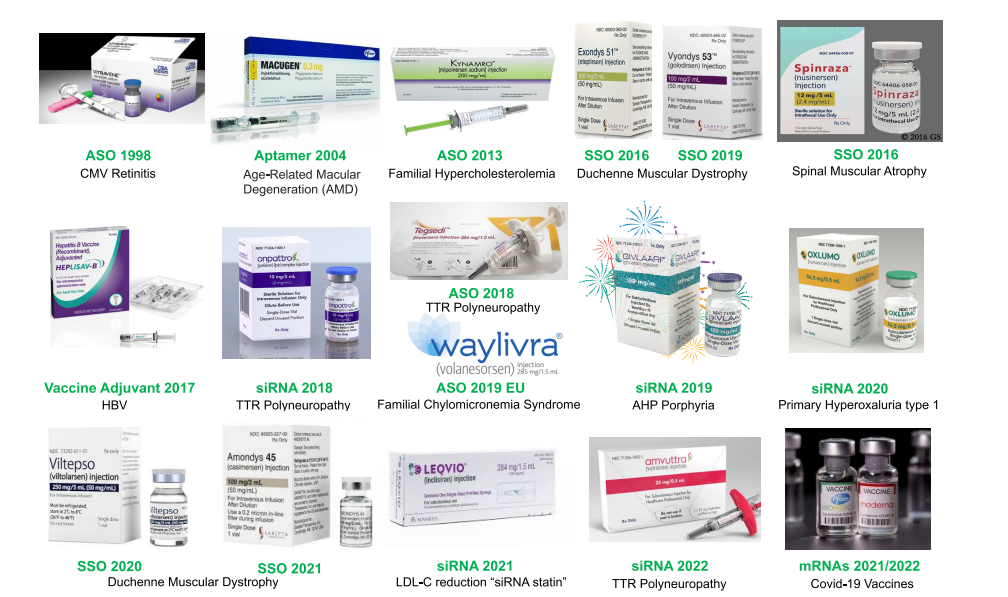
In the past 25 years, 18 oligonucleotide-based therapies have been approved to treat diseases like Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), and hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis. These therapies function via various mechanisms, including:
- Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs)
- Splice-Switching Oligonucleotides (SSOs)
- RNA Interference (RNAi)
- RNA Aptamers
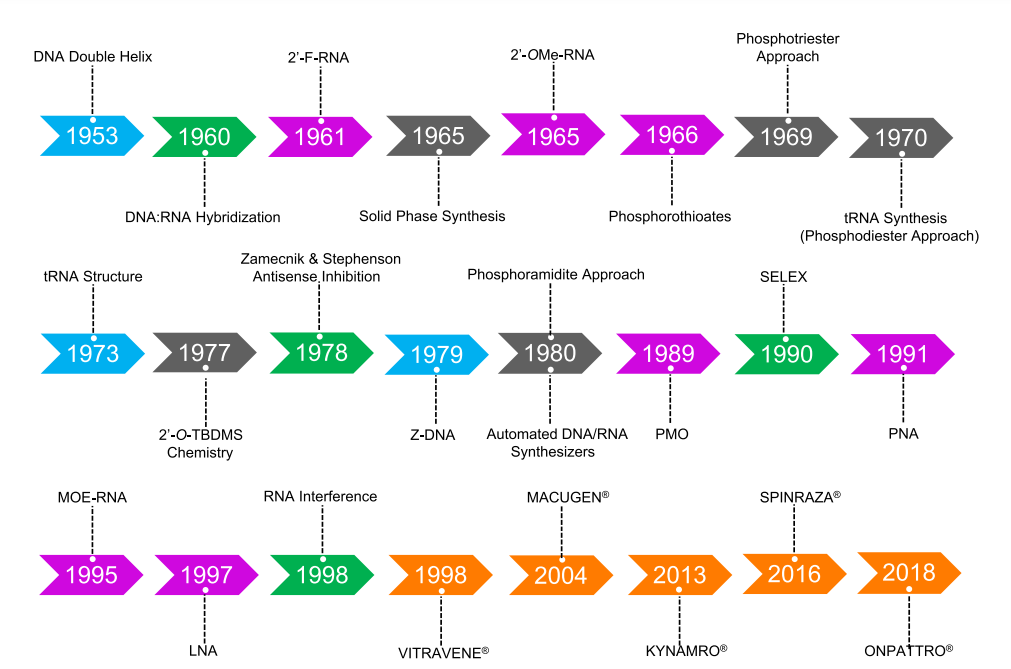
2. Historical Background
The origins of oligonucleotide therapeutics trace back to the 1950s and 1960s with foundational discoveries in DNA and RNA synthesis. Key pioneers, such as Todd and Khorana, contributed to understanding genetic coding, paving the way for molecular biology and nucleic acid-based medicine.
3. First-Generation Modifications
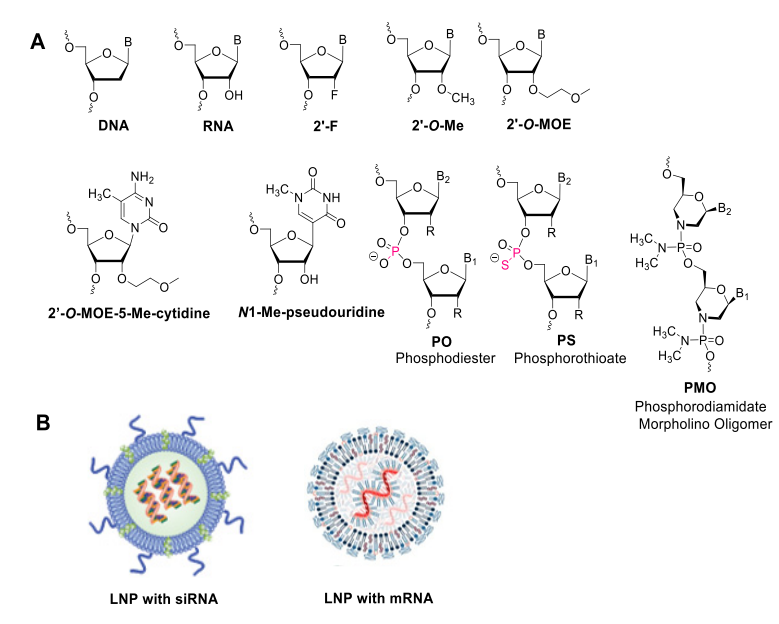
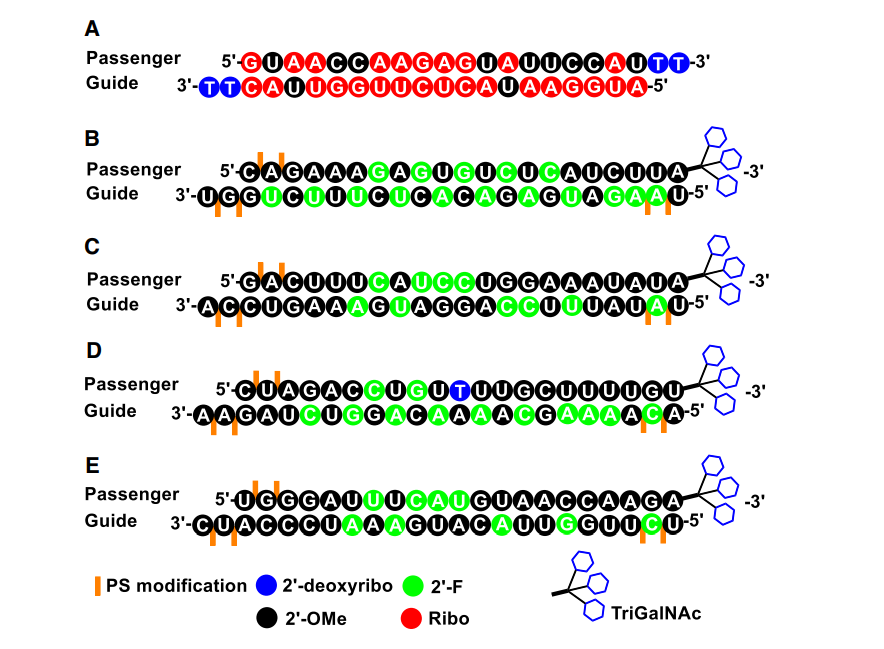
- Early oligonucleotides incorporated chemical modifications such as 2′-fluoro-RNA, 2′-O-methyl RNA, and phosphorothioates (PS).
- These changes enhanced stability and improved target affinity.
- The first FDA-approved antisense drug, VITRAVENE, emerged from these advances.
4. Second-Generation Modifications
The development of 2′-O-(2-methoxyethyl)-RNA (MOE-RNA) led to improved metabolic stability and efficacy. Key drugs developed with this technology include:
- KYNAMRO (for hypercholesterolemia)
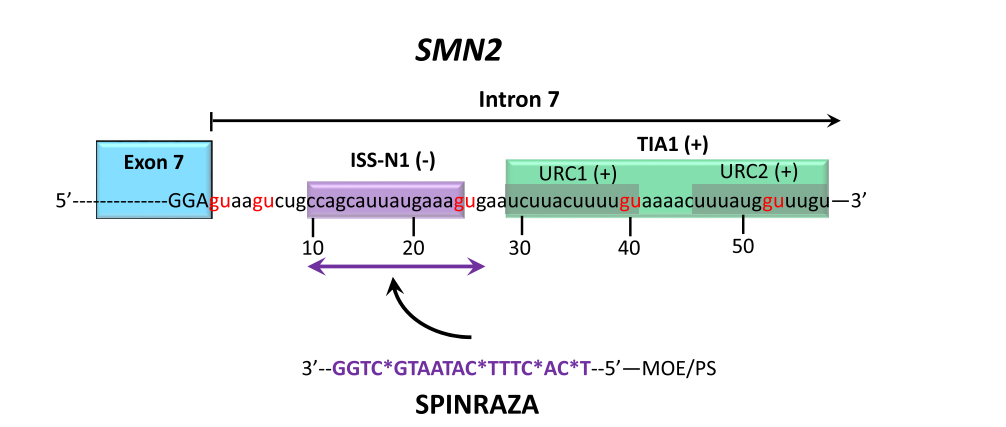
- SPINRAZA (for spinal muscular atrophy)
- TEGSEDI (for hereditary amyloidosis)
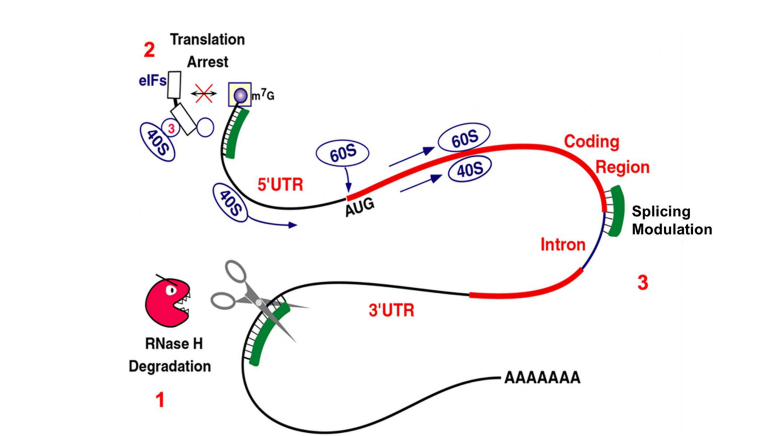
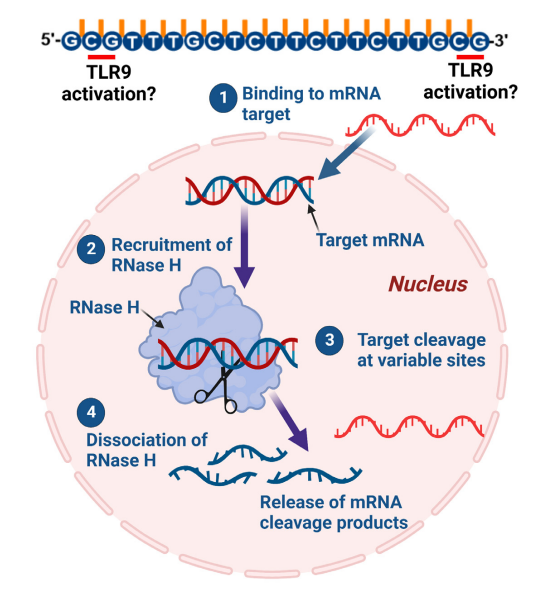
5. Mechanisms of Action
- ASOs: Block gene expression by binding to complementary RNA.
- SSOs: Modify RNA splicing to correct genetic errors.
- RNAi: Uses siRNA to silence genes.
- Aptamers: Bind to proteins to modulate their function.
6. Delivery Challenges and Solutions
- Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) enable efficient RNAi drug delivery.
- GalNAc conjugation enhances uptake in liver cells.
7. Future Prospects
Research continues on next-generation chemical modifications and targeted delivery mechanisms. New developments in receptor/ligand targeting may expand oligonucleotide therapies beyond liver tissues.
Conclusion
Oligonucleotide therapeutics continue to revolutionize medicine, with new chemical modifications and delivery strategies driving success. Their impact on treating genetic disorders remains a beacon of hope for future advancements.

| Published | 2023 Apr |
| Address | doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad067. |
| Authors | Martin Egli 1,* and Muthiah Manoharan |














