This paper introduces a novel therapeutic approach for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) using NS-089/NCNP-02, an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) designed to skip exon 44 of the dystrophin gene. DMD is a severe muscle disorder caused by mutations in the DMD gene, leading to a lack of dystrophin protein. Exon skipping helps restore the reading frame, enabling the production of a shorter but functional dystrophin protein.
Targeting Exon 44 for Dystrophin Restoration
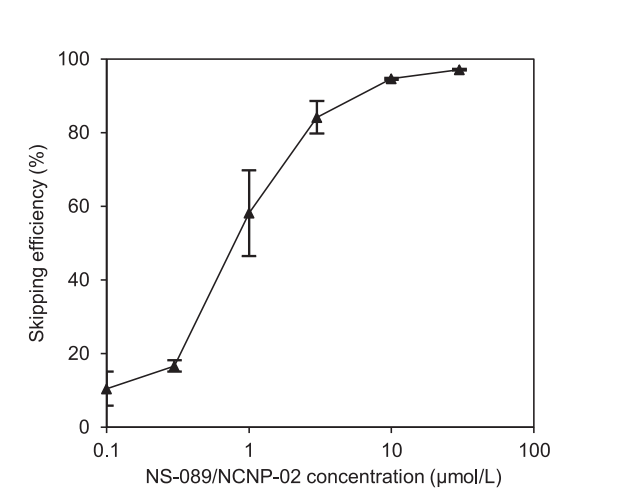
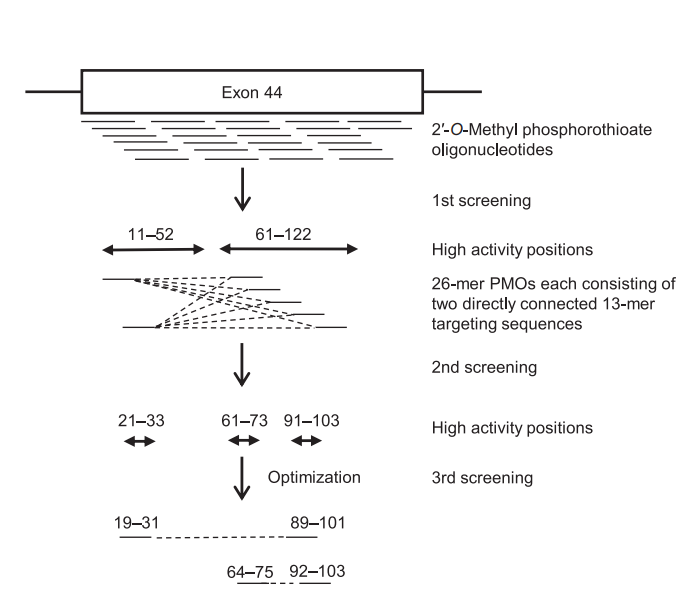
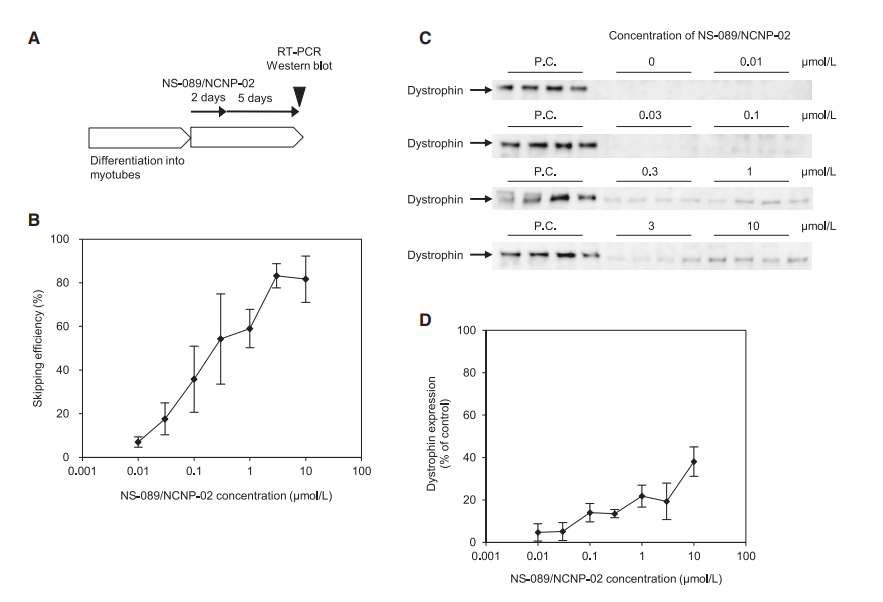
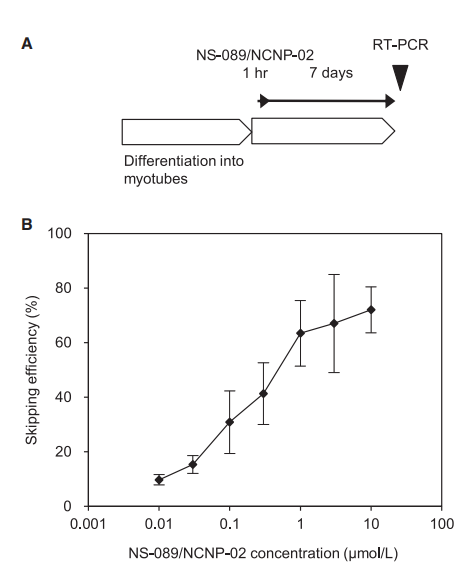
The authors focused on exon 44, a therapeutic target applicable to approximately 6% of DMD patients. Unlike previous exon-skipping drugs, which target a single sequence, NS-089/NCNP-02 targets two different sequences in exon 44, significantly improving exon-skipping efficiency. The in vitro studies showed that NS-089/NCNP-02 efficiently skipped exon 44 and restored dystrophin production in patient-derived cells.
In Vivo Studies in Animal Models
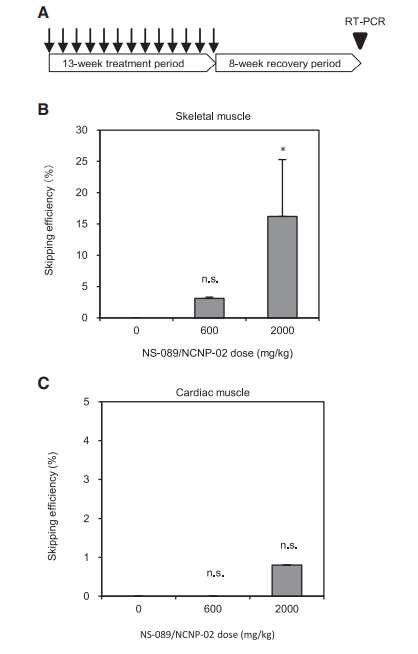
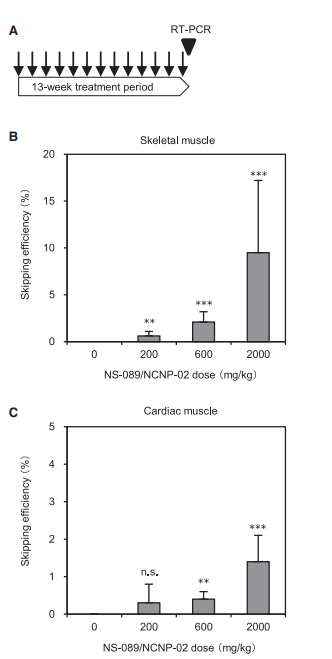
The study also included in vivo testing in cynomolgus monkeys. The results demonstrated that the drug induces exon skipping in both skeletal and cardiac muscles, although the effect was more pronounced in skeletal muscle. This suggests the drug's potential for systemic therapy, where it can improve muscle function across different tissues.
Conclusion and Future Prospects
This dual-targeting ASO offers a promising new therapeutic option for patients with DMD. Its ability to skip exon 44 and efficiently restore dystrophin expression could significantly improve outcomes for those affected by this genetic disorder. Further clinical trials are necessary to validate its effectiveness and ensure long-term safety.




| Information | Details |
| Authors | Naoki Watanabe, Yuichiro Tone, Tetsuya Nagata, Satoru Masuda, Takashi Saito, Norio Motohashi, Kazuchika Takagaki, Yoshitsugu Aoki, Shin’ichi Takeda |
| Corresponding Author | Shin’ichi Takeda |
| Article Title | Exon 44 skipping in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: NS-089/NCNP-02, a dual-targeting antisense oligonucleotide |
| Publication Date | Dec-23 |
| Journal Name | Molecular Therapy: Nucleic Acids |
| Keywords | #DMD, #ExonSkipping, #ASO, #MuscleRegeneration, #Therapeutics |
| Methods Used | PCR, Western Blotting, In Vivo Animal Studies |
| DOI | 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.102034 |














