Understanding the Challenge of FSHD:
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) is a genetic disorder caused by the aberrant expression of the DUX4 gene in muscle cells. This leads to progressive muscle weakness and degeneration. Unfortunately, no molecular therapy currently exists to stop or slow the disease’s progression.
The Potential of Antisense Oligonucleotide (ASO) Therapy:
This study investigates the efficacy of a novel antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) designed to suppress DUX4 expression in an ACTA1-MCM;FLExDUX4 mouse model that mimics FSHD. The ASO treatment aims to reduce DUX4 transcript levels, thereby preventing its toxic downstream effects.
Study Design and ASO Administration:
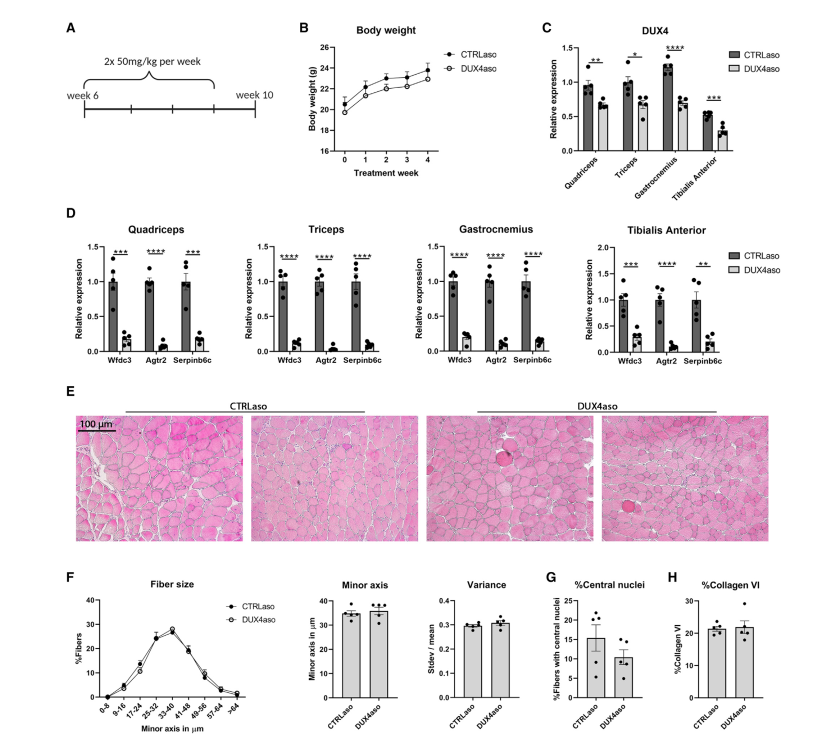
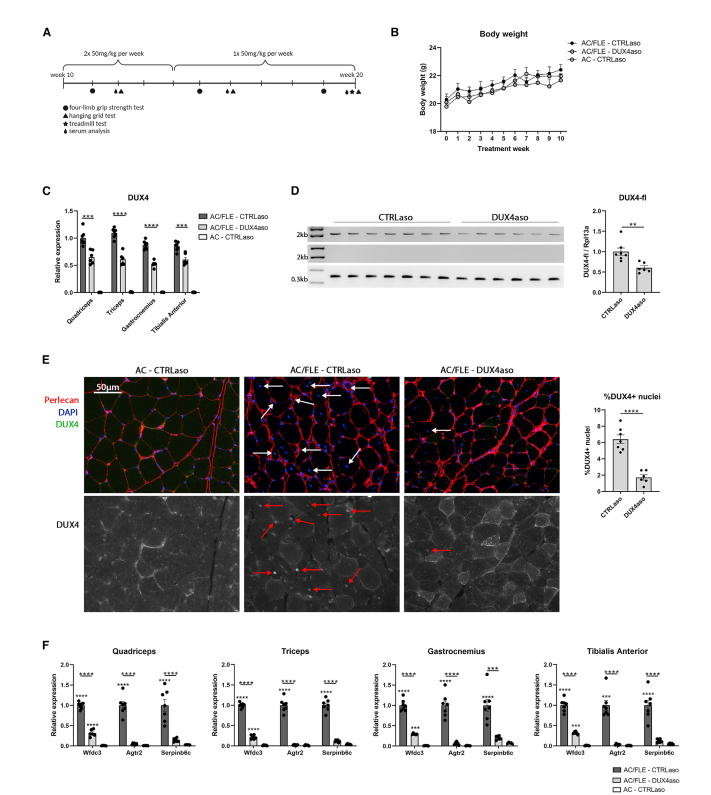
The ASO therapy was delivered via subcutaneous injections, allowing for systemic distribution throughout the muscle tissues. Researchers evaluated the therapy’s impact on:
- DUX4 transcript reduction: Measured through gene expression analysis.
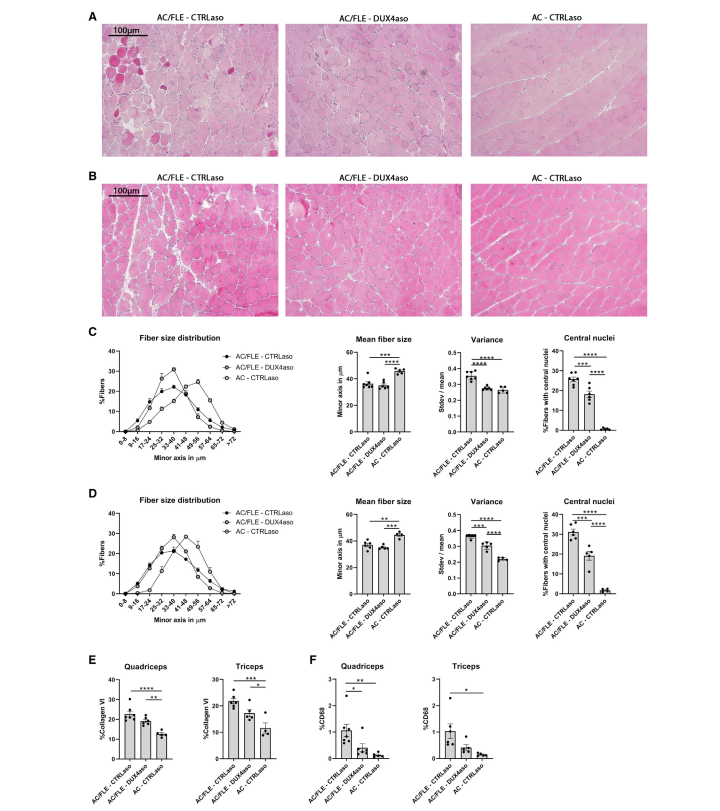
- Muscle pathology improvement: Assessed via histological examination.
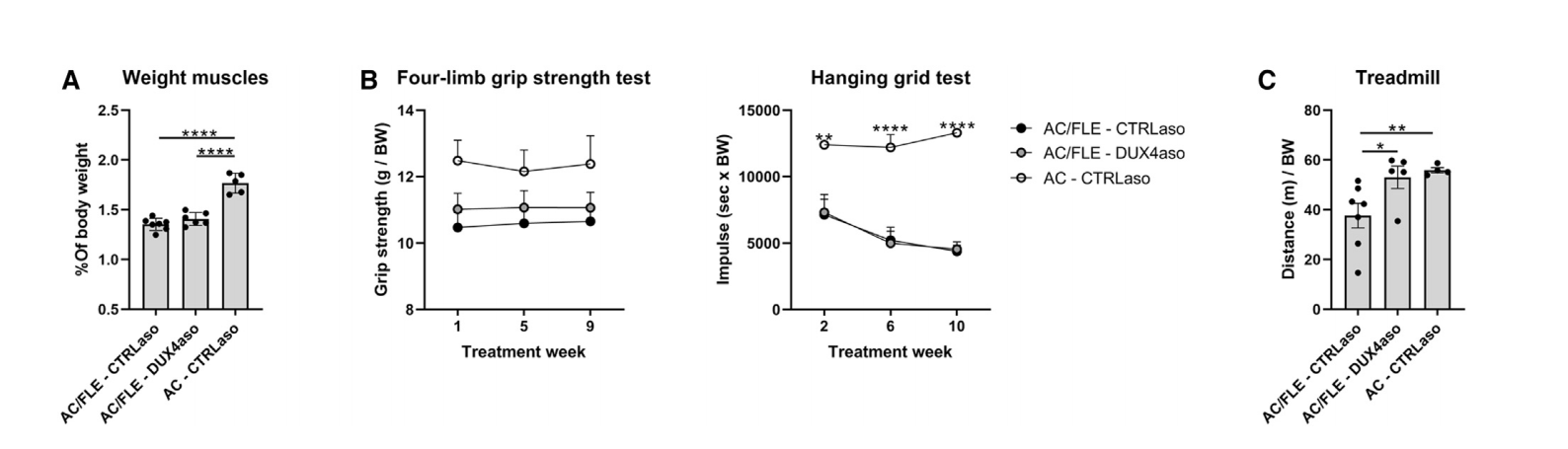
- Functional muscle performance: Evaluated through muscle strength testing.
Key Findings:
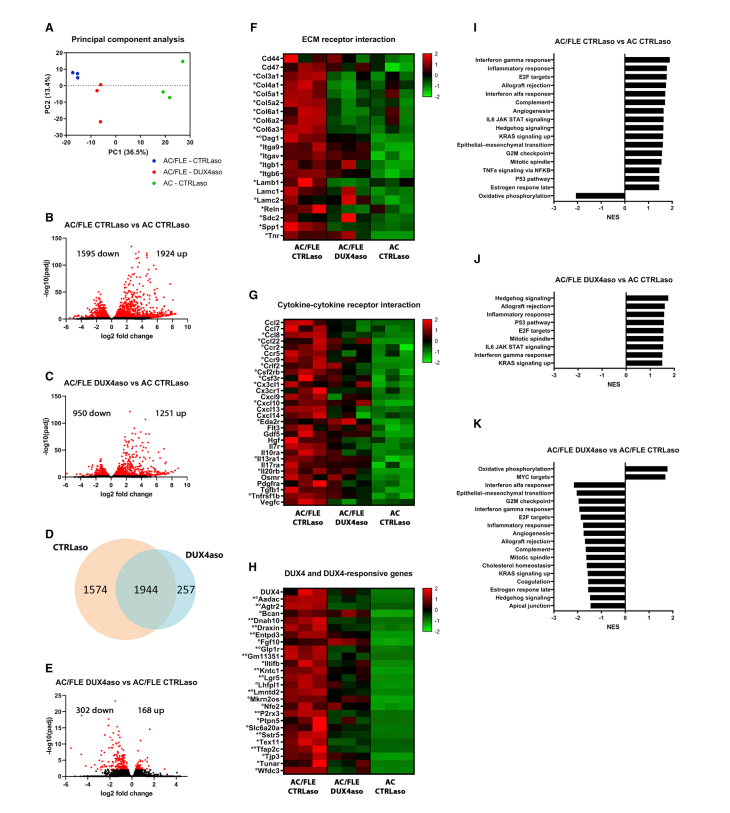
The ASO treatment successfully reduced DUX4 expression and prevented the activation of DUX4 target genes. Additionally, it alleviated muscle inflammation and fibrosis, key pathological features of FSHD.
However, muscle strength did not significantly improve, and some disease features, such as loss of muscle mass and central nuclei formation, remained unchanged. This suggests that while ASO therapy provides partial benefits, it may not fully restore muscle function.
Conclusion and Future Directions:
Systemic ASO therapy targeting DUX4 presents a promising approach for FSHD treatment. However, enhancing ASO delivery and improving its ability to restore muscle strength are crucial next steps. Researchers suggest that early intervention in the disease process may prevent more severe muscle deterioration.










| Category | Details |
| Authors (All) | Linde F. Bouwman, Bianca den Hamer, Anita van den Heuvel, Marnix Franken, Michaela Jackson, Chrissa A. Dwyer, Stephen J. Tapscott, Frank Rigo, Silvère M. van der Maarel, Jessica C. de Greef |
| Corresponding Author | Jessica C. de Greef |
| Article Title | Systemic delivery of a DUX4-targeting antisense oligonucleotide to treat facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy |
| Publication Date | Dec-21 |
| Journal Name | Molecular Therapy: Nucleic Acids |
| Keywords | #DUX4 #FSHD #AntisenseOligonucleotide #TherapeuticStrategy #MusclePathology |
| Methods Used | ASO systemic injection, RNA quantification, PCR, functional muscle tests |
| DOI | 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.09.010 |














