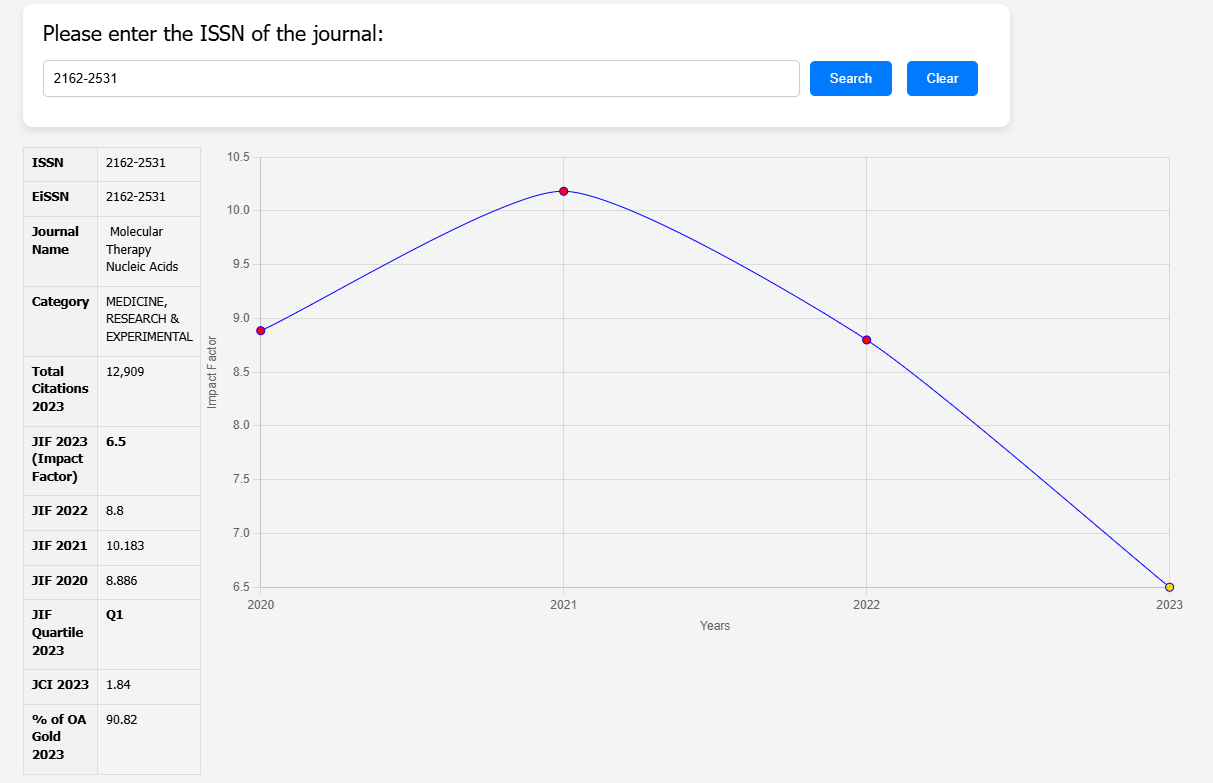
Introduction
This study addresses the challenges of aberrant pre-mRNA splicing in Pompe disease, caused by pathogenic variants in the acid α-glucosidase (GAA) gene. These variants often lead to the use of cryptic splice sites, disrupting protein production. The research proposes a pipeline to identify splicing defects and correct them using antisense oligonucleotides (AONs).
Methods
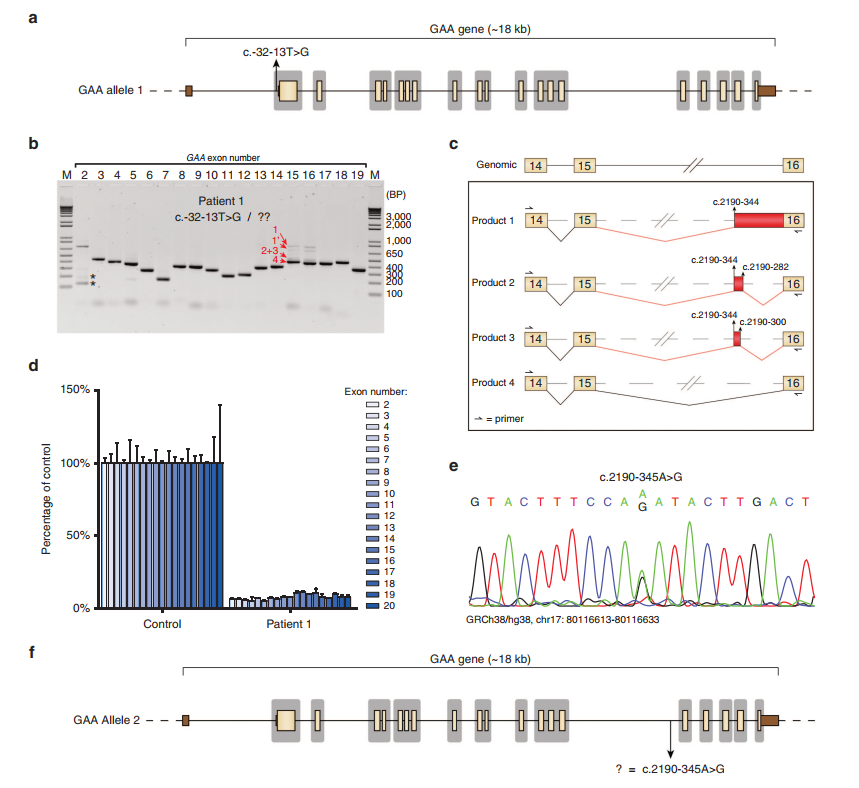
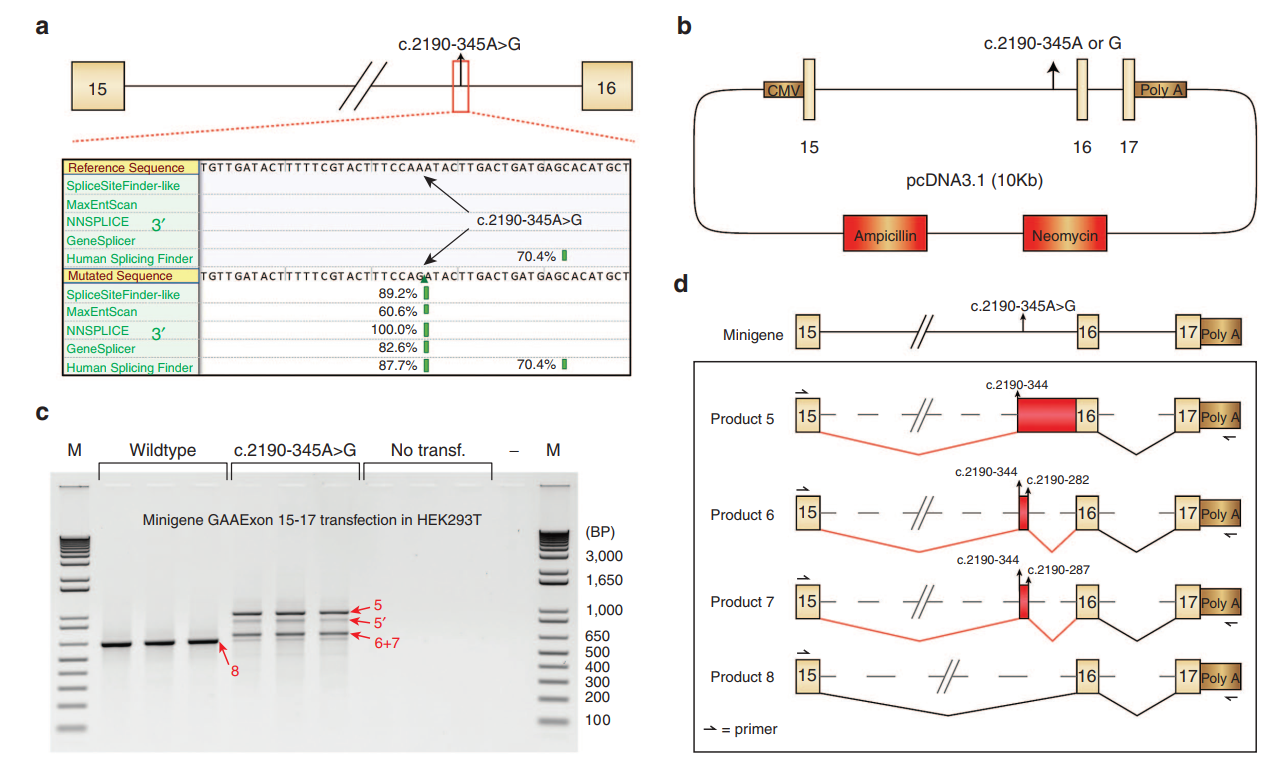
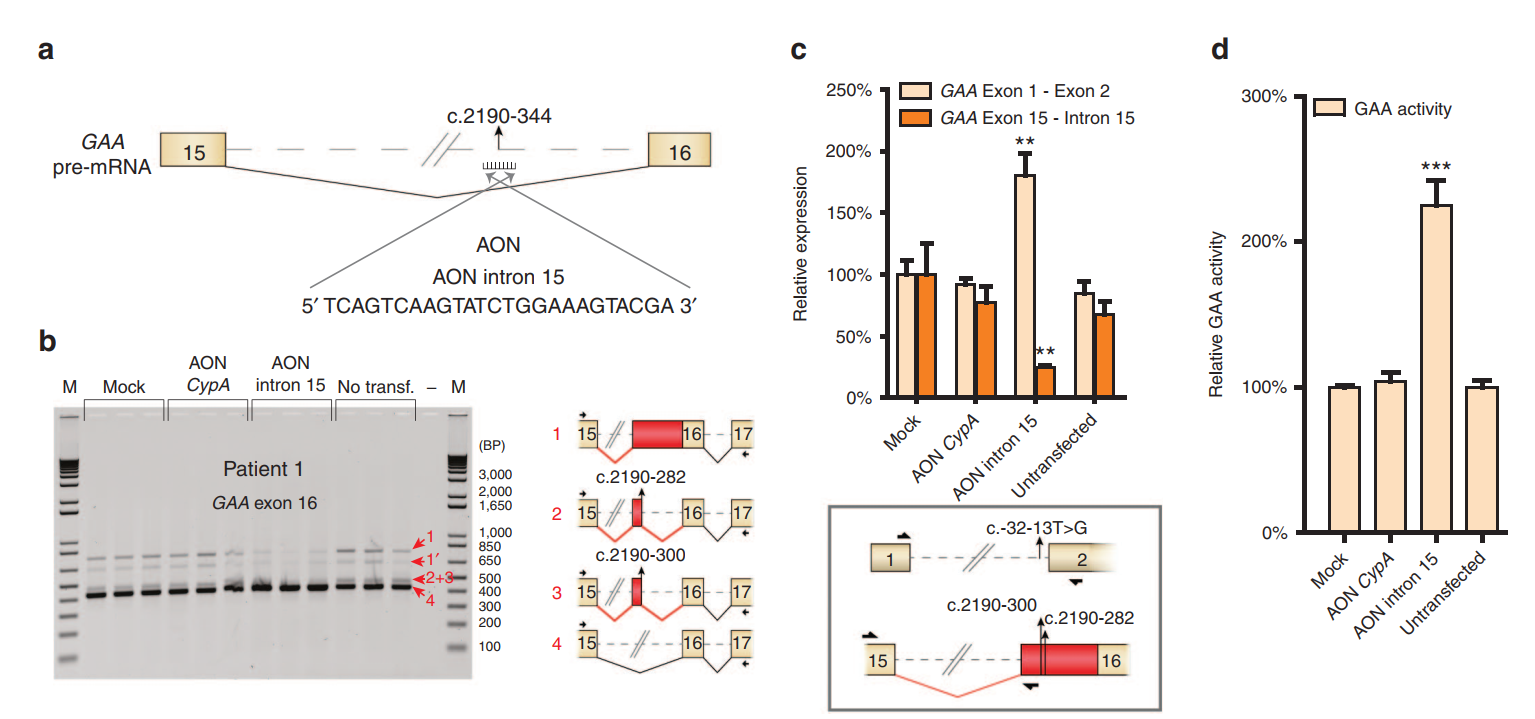
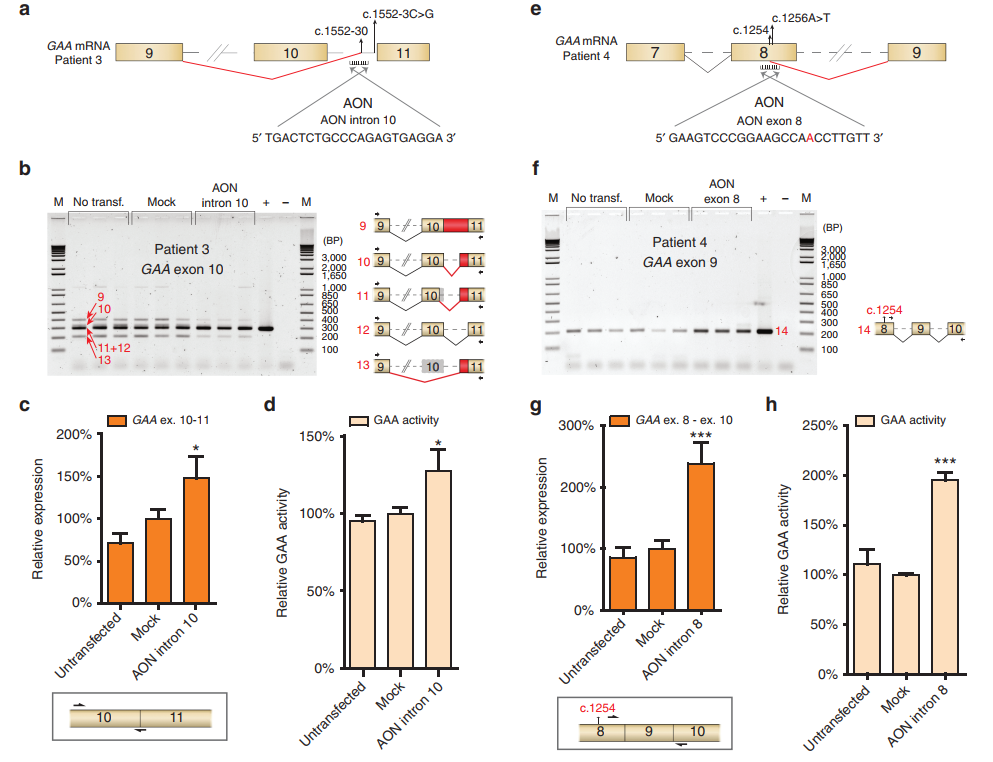
The team developed a splicing assay to detect aberrant splicing patterns in patient-derived fibroblasts. They identified three main types of cryptic splicing events. The study highlights cases where pathogenic variants either generate new splice sites or weaken canonical ones, leading to cryptic site utilization.
Key Findings
Using AONs, the researchers successfully redirected splicing from cryptic sites back to canonical ones. This correction increased GAA enzyme activity, which is crucial for reducing disease severity. They demonstrated this approach in fibroblast samples from several patients, showing promising therapeutic potential.
Challenges
The study discusses challenges, such as predicting splicing behavior and ensuring efficient AON delivery to target tissues. They also emphasize the advantages of their PCR-based assay, which is cost-effective and reliable for identifying splicing defects.
Clinical Significance
The research supports AONs as a potential personalized medicine approach for Pompe disease, especially for the adult-onset form, where skeletal muscle is primarily affected. The success of AONs in this context could lead to more accessible and effective treatments compared to current enzyme replacement therapy.
Conclusion
Overall, this work represents a significant step toward understanding and treating genetic disorders that involve splicing errors, using precise, targeted genetic tools. Further studies are needed to optimize delivery methods and long-term efficacy.


| Field | Details |
| Authors | Atze J. Bergsma, Stijn L.M. in ’t Groen, Frans W. Verheijen, Ans T. van der Ploeg, W.W.M. Pim Pijnappel |
| Corresponding Author | W.W.M. Pim Pijnappel (w.pijnappel@erasmusmc.nl) |
| Article Title | From Cryptic Toward Canonical Pre-mRNA Splicing in Pompe Disease: a Pipeline for the Development of Antisense Oligonucleotides |
| Publication Date | 13-Sep-16 |
| Journal Name | Molecular Therapy—Nucleic Acids |
| Keywords | cryptic splice site, morpholino antisense oligonucleotides, muscle, Pompe disease, splicing correction |
| Methods Used | Splicing assays, RT-qPCR, minigene analysis, AON treatment, fibroblast culture |
| DOI | 10.1038/mtna.2016.75 |