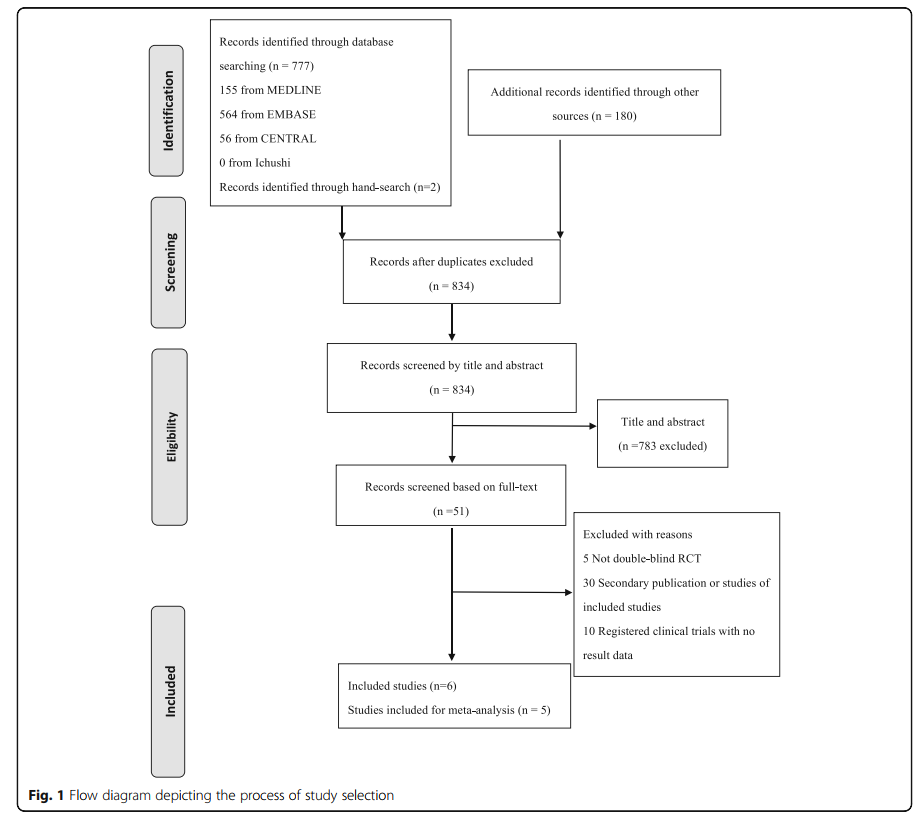
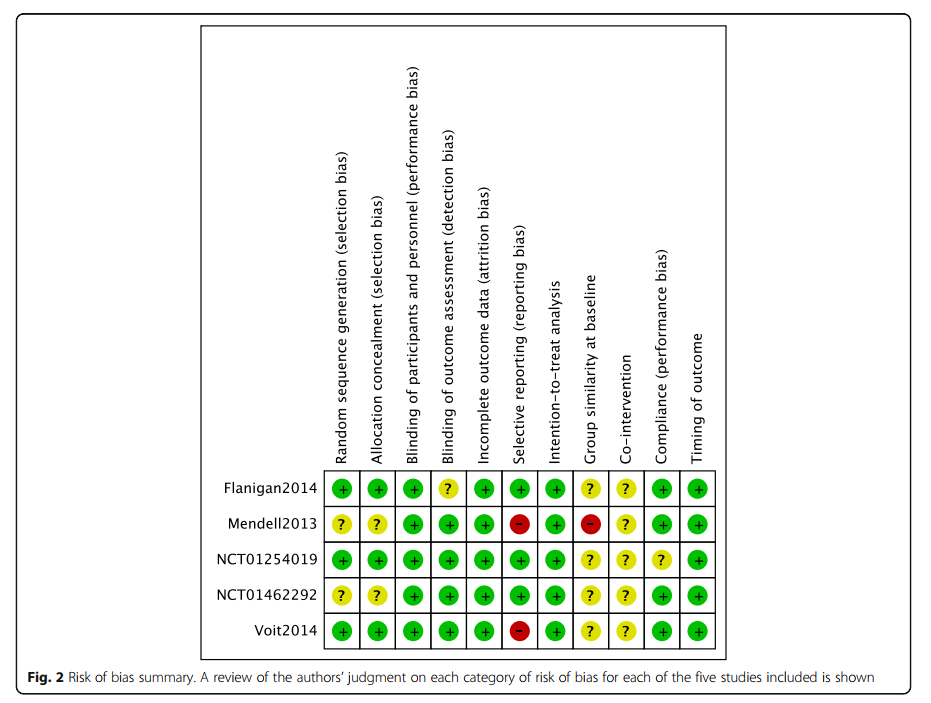
Exon skipping is a promising therapeutic strategy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), a severe genetic disorder. By using antisense oligonucleotides (AOs), this method aims to restore a partially functional dystrophin protein. The study conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of five randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving 322 participants, focusing on two drugs: eteplirsen and drisapersen. The analysis evaluated outcomes such as the 6-minute walk test (6MWT), North Star Ambulatory Assessment (NSAA) scores, and adverse events after 24 weeks.
Key Findings
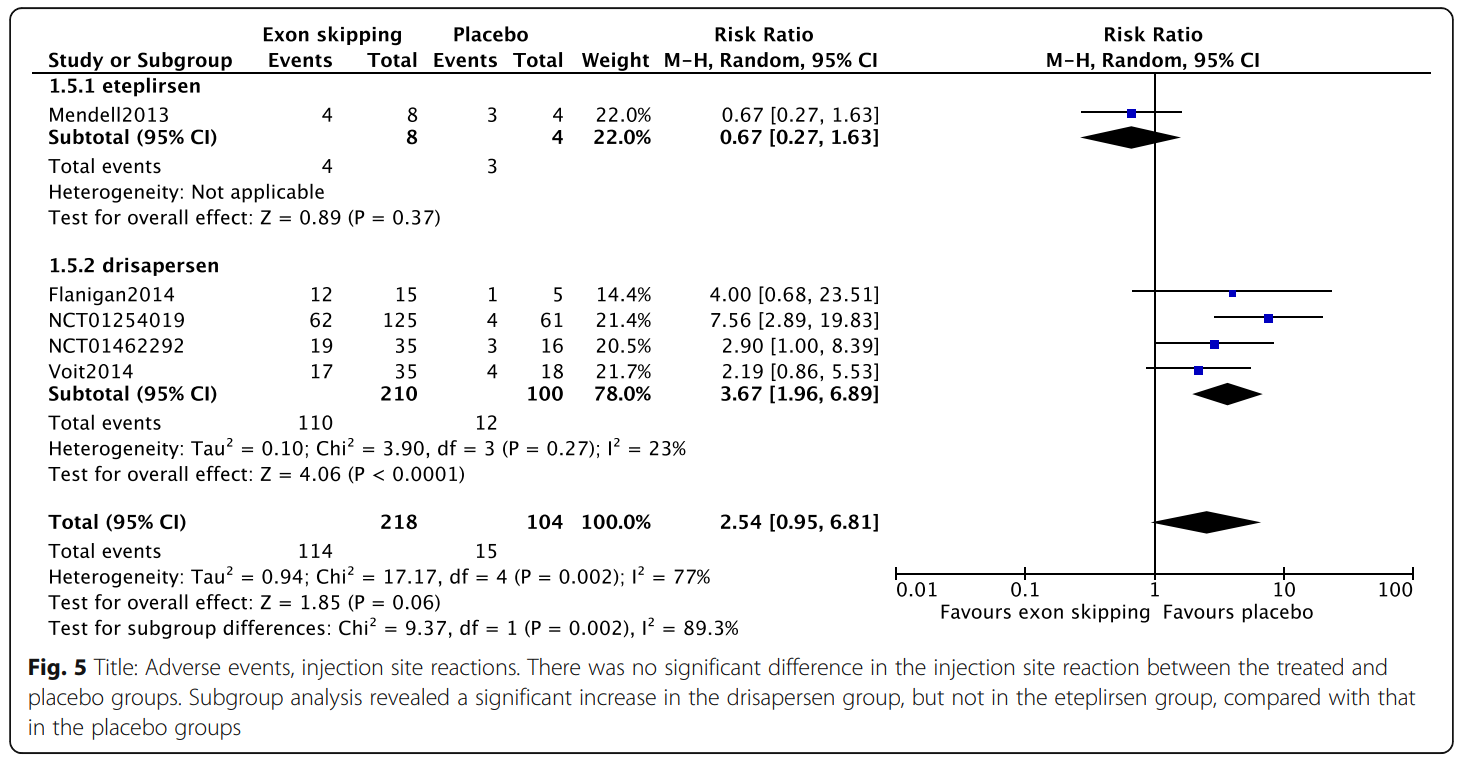
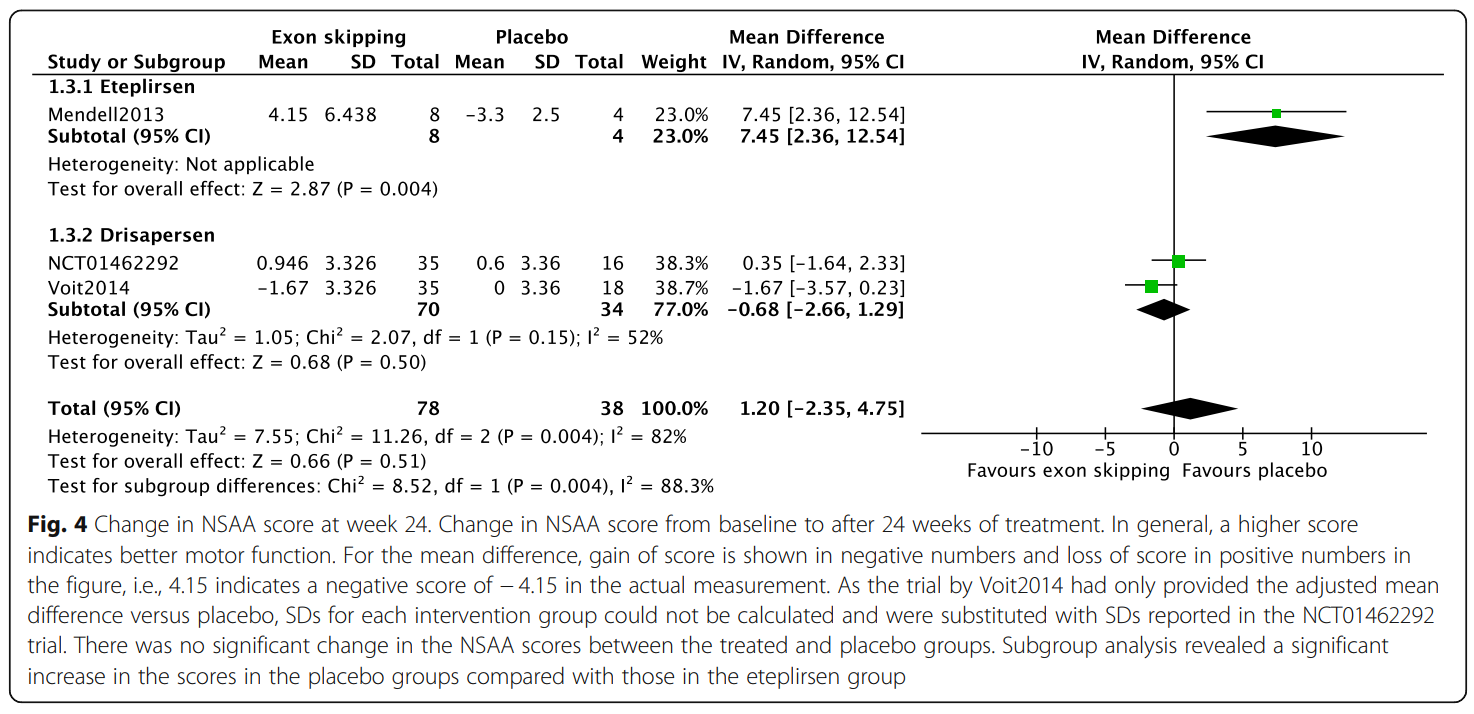
Results indicated that exon-skipping drugs do not significantly improve clinical outcomes compared to placebo. Specifically, changes in the 6MWT distance and NSAA scores were negligible. However, subgroup analysis of drisapersen at a specific dose (6 mg/kg weekly) showed minor improvement in walking ability but also revealed significant side effects, including injection site reactions and renal toxicity.
Adverse Effects
Eteplirsen demonstrated fewer adverse effects but lacked strong evidence of efficacy due to limited data. The review highlights the challenges of conducting large-scale studies for rare diseases like DMD, emphasizing the need for more robust, prospectively planned trials and real-world data collection to clarify the efficacy of exon-skipping therapies.
Conclusion
The study concludes that while exon skipping remains a potential treatment, current evidence does not fully support its clinical application, especially due to the safety concerns surrounding drisapersen. Ongoing research and longer-term data are essential to determine the true impact of these therapies on disease progression and patient outcomes.


| Category | Details |
| Authors | Yuko Shimizu-Motohashi, Terumi Murakami, En Kimura, Hirofumi Komaki, Norio Watanabe |
| Corresponding Author | Norio Watanabe (watanabe.norio.6x@kyoto-u.ac.jp) |
| Article Title | Exon skipping for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a systematic review and meta-analysis |
| Publication Date | 10-Jul-05 |
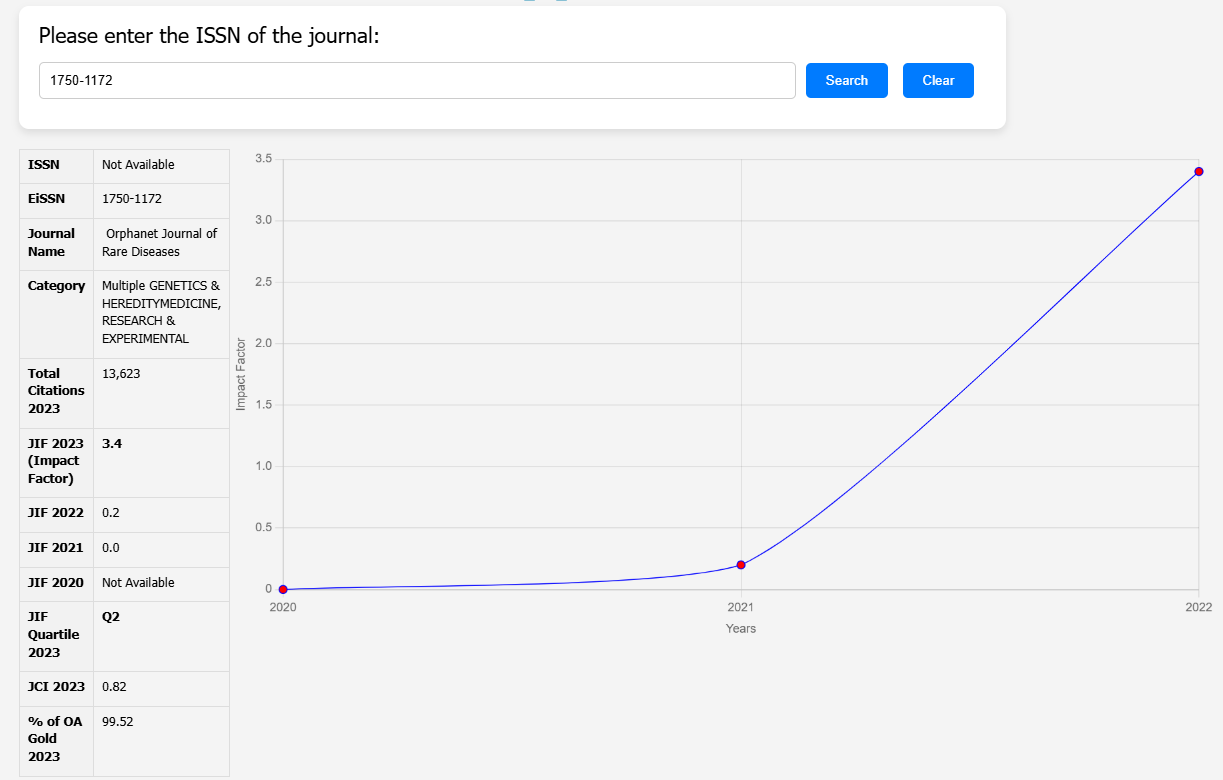
| Journal Name | Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases |
| Keywords | Exon skipping, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, eteplirsen, drisapersen, randomized controlled trial, 6-minute walk test, antisense oligonucleotides, meta-analysis |
| Methods Used | Systematic review, meta-analysis, randomized controlled trials, subgroup analysis, risk of bias assessment |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-018-0834-2 |