Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe genetic disorder caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene, leading to muscle degeneration and early death. Antisense oligonucleotides (AONs) are promising therapeutic agents designed to skip faulty exons in the dystrophin gene and restore functional protein expression.
Study Objective and Approach
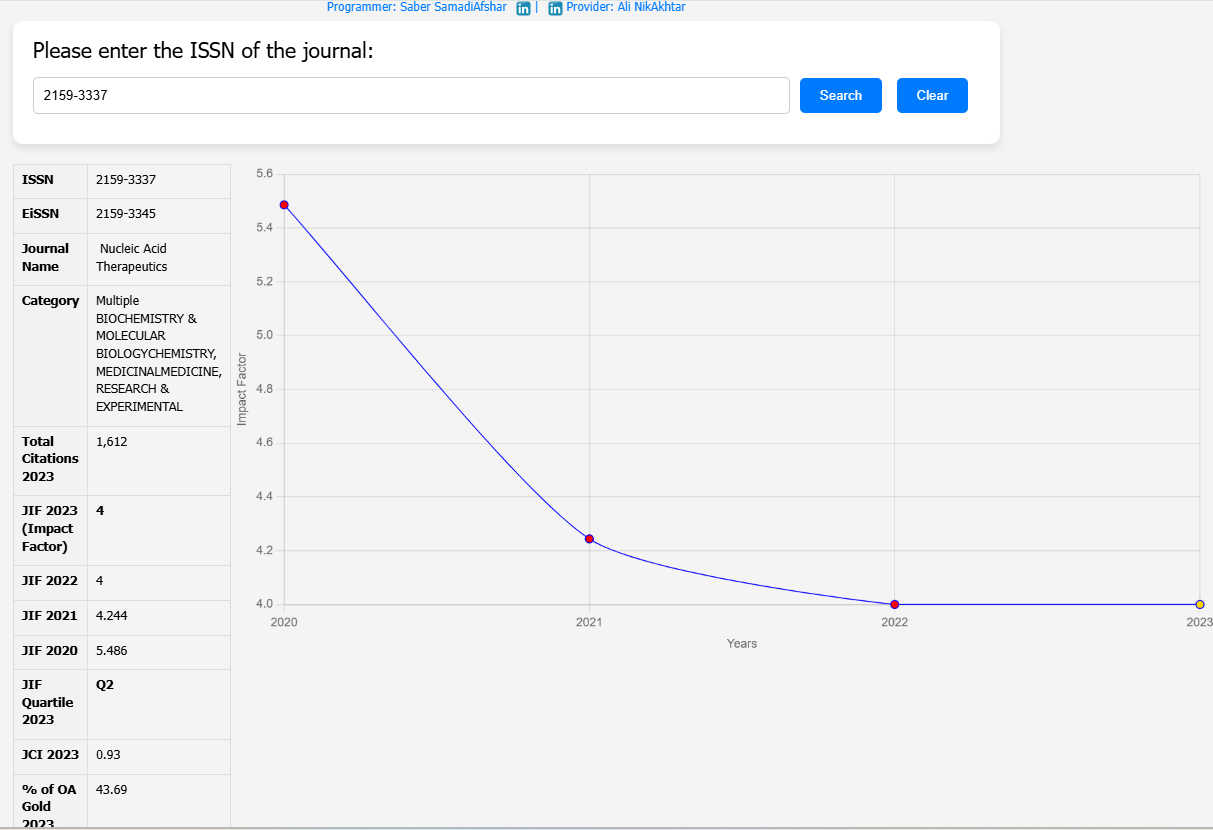
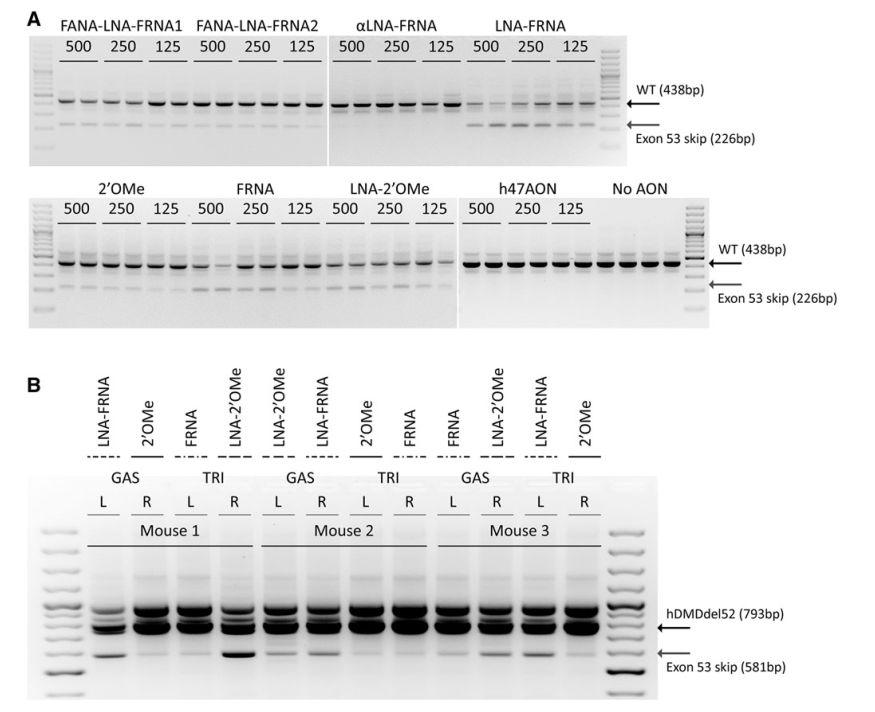
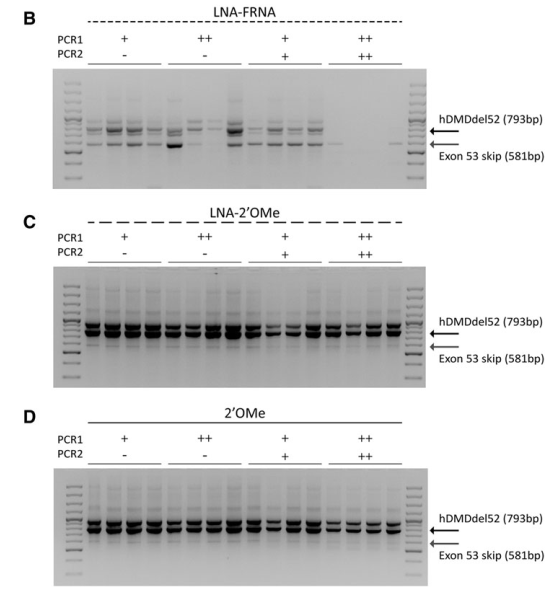
This study evaluated the efficiency of AONs targeting exon 53 of the dystrophin gene in a mouse model, using chemically modified AONs to enhance exon skipping and protein restoration. The study compared different AON modifications, including 2′-O-methyl (2′OMe), LNA-2′OMe, and LNA-FRNA, in both human myoblast cultures and a specialized mouse model (hDMDdel52/mdx).
Methods and Key Findings
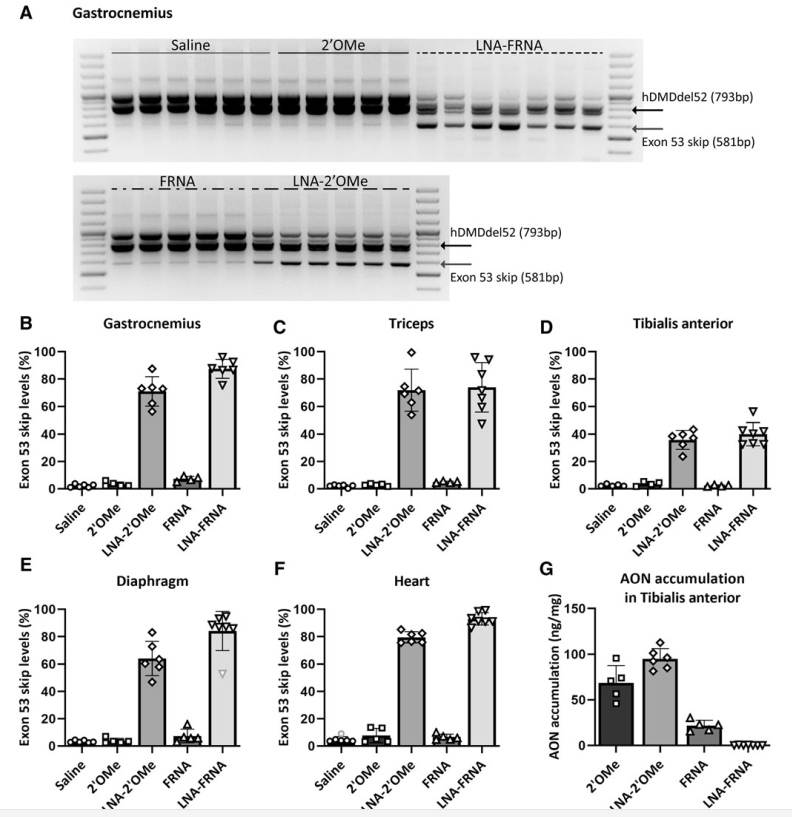
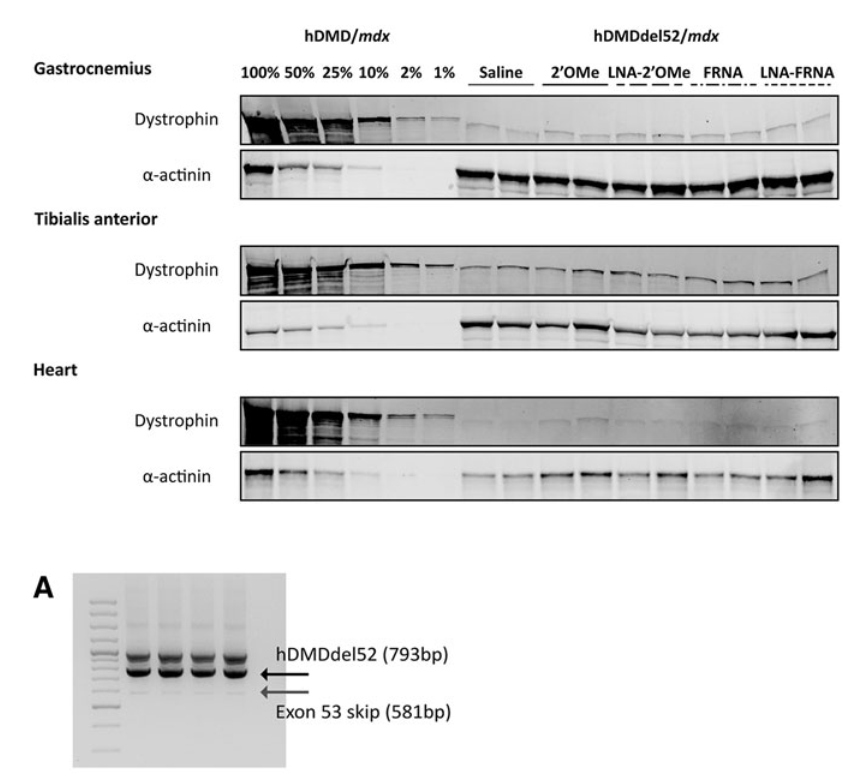
Systemic and local injections of AONs were performed, followed by molecular and protein analyses. While high levels of exon skipping were observed with certain AONs (e.g., LNA-FRNA, LNA-2′OMe), actual dystrophin restoration remained negligible. This discrepancy was attributed to AON interference during RNA analysis, leading to an overestimation of exon skipping efficiency.
LNA-modified AONs bind strongly to RNA, interfering with cDNA synthesis and amplification. Adjustments such as higher RNA denaturation temperatures (95°C) partially mitigated these issues, improving the accuracy of exon-skipping detection.
Conclusion and Future Directions
While AONs show potential for exon skipping, further refinement in RNA analysis and long-term studies are essential to confirm therapeutic benefits. Chemically modified AONs, particularly those with LNA modifications, enhance exon skipping efficiency but require careful assessment of therapeutic outcomes.
Optimization of AON designs and exploration of alternative exon targets are recommended to improve therapeutic efficacy for DMD.











| Field | Details |
| Authors | Sarah Engelbeen, Daniel O’Reilly, Davy Van De Vijver, Ingrid Verhaart, Maaike van Putten, Vignesh Hariharan, Matthew Hassler, Anastasia Khvorova, Masad J. Damha, Annemieke Aartsma-Rus |
| Corresponding Author | Masad J. Damha, Annemieke Aartsma-Rus |
| Article Title | Challenges of Assessing Exon 53 Skipping of the Human DMD Transcript with Locked Nucleic Acid-Modified Antisense Oligonucleotides in a Mouse Model for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy |
| Publication Date | 15-Jul-05 |
| Journal Name | Nucleic Acid Therapeutics |
| Keywords | Efficacy, locked nucleic acid, LNA, preclinical studies, exon skipping |
| Methods Used | In vitro analysis, in vivo validation, RT-PCR, western blot, AON synthesis, qPCR |
| DOI | 10.1089/nat.2023.0038 |