Overview
This study evaluated the effectiveness of prenatal Exome Sequencing (ES) in detecting genetic abnormalities in fetuses with various ultrasound findings, even in cases where ES was not initially indicated. The researchers compared ES with chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) to identify Copy Number Variants (CNVs) and monogenic disorders.
Key Findings
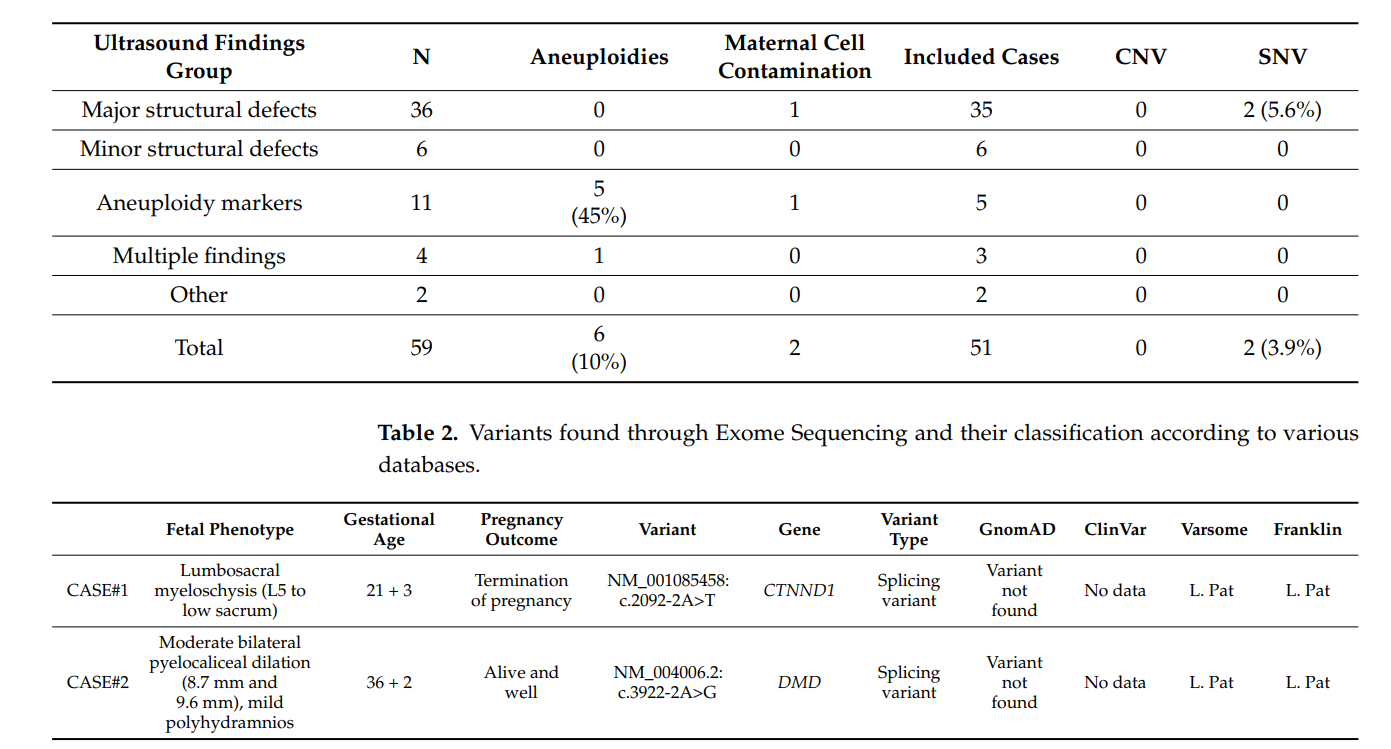
- Genetic Abnormalities Detected: Among 59 pregnancies, common aneuploidies were identified in 10% of cases using QF-PCR.
- CMA vs. ES: No pathogenic CNVs were detected through CMA, but Exome Sequencing identified monogenic disorders in 3.9% of cases, even when unrelated to ultrasound findings.
- Expanded Gene Analysis: Limiting ES to targeted gene panels did not increase detection rates, but including a broader range of genes revealed additional clinically relevant monogenic disorders.
Conclusion
This study suggests that Exome Sequencing could be valuable in prenatal diagnostics, especially when CMA results are normal. However, the decision to perform ES should be carefully considered due to the potential for incidental findings. Future research should explore expanding ES applications to maximize diagnostic accuracy.

| Published | 12/28/2023 |
| Address | https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010181 |
| Authors | Antoni Borrell 1,* , Elena Ordoñez 2, Montse Pauta 3, Juan Otaño 1 , Fernanda Paz-y-Miño 1, Mafalda de Almeida 2, Miriam León 2 and Vincenzo Cirigliano 2 |














