Overview
This article provides a detailed review of the latest advancements in gene-targeting therapies for Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), a severe genetic disorder that leads to motor neuron loss, causing muscle weakness, loss of mobility, and potentially death if untreated.
Key Points
- SMA Overview:
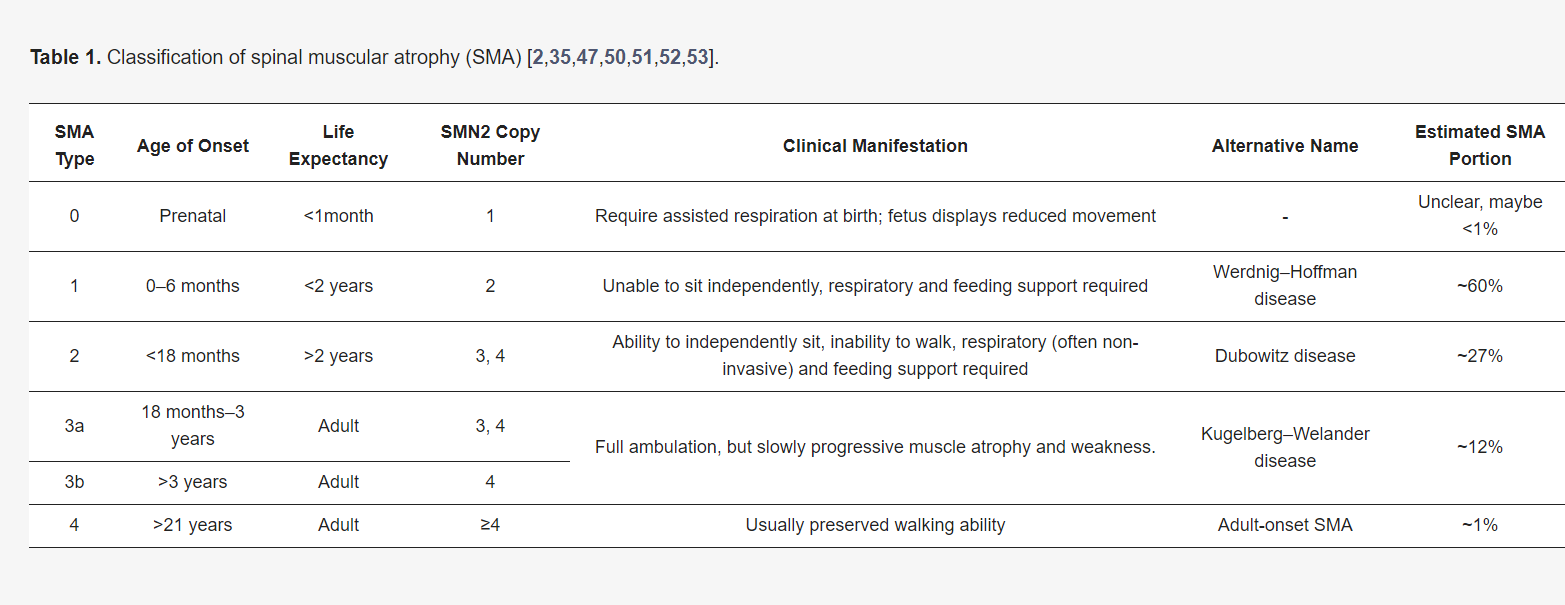
- Cause: SMA is caused by mutations in the SMN1 gene, leading to a deficiency in the SMN protein, which is essential for motor neuron survival.
- SMN2 Compensation: Humans have a similar gene, SMN2, which partially compensates for the loss of SMN1, but not enough to prevent the disease.
- Therapeutic Approaches:
- Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs): Drugs like Nusinersen modify SMN2 splicing to produce more functional SMN protein.
- Gene Replacement Therapy: Onasemnogene Abeparvovec delivers a functional copy of the SMN1 gene to patients.
- Small Molecules: Risdiplam is an oral drug that promotes exon 7 inclusion in SMN2, boosting SMN protein levels.
- Challenges in SMA Treatment:
- Multi-Systemic Effects: SMA affects multiple organs, but current treatments primarily focus on increasing SMN protein levels.
- Need for Combination Therapy: The article suggests that combination therapies may be necessary to address both SMN-related and SMN-independent disease mechanisms.
- Future Directions:
- Exploring New Treatments: Ongoing research focuses on alternative treatments beyond SMN protein restoration.
- Multi-Faceted Therapeutic Approaches: Addressing motor neuron survival, muscle function, and systemic symptoms is crucial.
Conclusion
This article highlights significant progress in SMA treatment, emphasizing the importance of increasing SMN protein levels. However, while current treatments are promising, they are not a complete cure. Future research must explore additional therapeutic methods to manage SMA more effectively.


| Published | 7/30/2024 |
| Address | https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15080999 |
| Authors | Umme Sabrina Haque, Toshifumi Yokota |














