more
Exon skipping
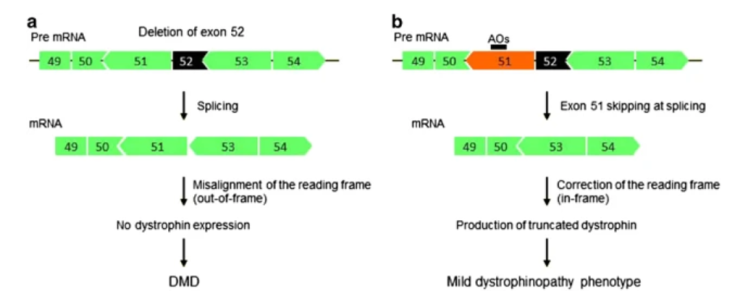
This article explains exon skipping, a genetic technique for treating Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) by restoring the dystrophin protein using antisense oligonucleotides.
more
Several muscle diseases 5 : DYSF (Dysferlin) , Miyoshi Myopathy
This article explores DYSF mutations and Miyoshi Myopathy, detailing the role of dysferlin in muscle membrane repair and how its deficiency leads to muscle degeneration.
more
Several muscle diseases 4 : Skeletal Muscle FSHD

This article discusses facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD), its genetic mechanisms, symptoms, and current research on potential treatments.
more
Several muscle diseases 3: LGMD2I, LGMD2B

This article discusses LGMD2I and LGMD2B, two subtypes of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, their genetic causes, symptoms, and current management options.
more
Several muscle diseases 2: ZNF9 BMD MC-AD DMD TMD

This article discusses multiple muscle diseases, including ZNF9, BMD, MC-AD, DMD, and TMD, highlighting their genetic causes, symptoms, and disease progression.
more
Several muscle diseases 1: DM1 DM2 DMx DM-like DMPK

This article explores various muscle diseases, including DM1, DM2, and DMx, detailing their genetic causes, symptoms, and the role of DMPK in myotonic dystrophy.
more
Recent Posts
Categories
- DystroBlog | Neuromuscular Disease Research & News(96)
- Christopher W Ward(1)
- Jeffrey Chamberlain(2)
- Douglas Millay(1)
- Luis Garcia(1)
- Vincent Mouly(1)
- Bible(1)
- Yusuke Echigoya(2)
- Yuko Shimizu-Motohashi(1)
- Yu-Chiang Lai(1)
- Ype Elgersma(1)
- Yoshitsugu Aoki(1)
- Yetrib Hathout(1)
- Yasuhiro Yamada(1)
- W. David Arnold(1)
- Volker Straub(3)
- Virginia Arechavala-Gomeza(1)
- Vahab Soleimani(1)
- Utkarsh J. Dang(2)
- Toshifumi Yokota(13)
- Tony Kwan(1)
- Tobias Ruck(3)
- Tim Hagenacker(1)
- Thomas Sejersen(1)
- Theodore Perkins(1)
- Terry Partridge(1)
- Steve Wilton(1)
- Stephen Tapscott(1)
- Silvere van der Maarel(1)
- Shin’ichi Takeda(2)
- Ryszard Kole(1)
- Robert Weiss(1)
- Rob W.J. Collin(1)
- Rita Horvath(2)
- Renato Dulbecco(2)
- Rashmi Kothary(1)
- Rafal Czapiewski(1)
- Pim Pijnappel(1)
- Peter Meinke(1)
- Peter F M Van der Ven(2)
- Paula R. Clemens(2)
- Norio Motohashi(1)
- Muthiah Manoharan(1)
- Michela Guglieri(2)
- Michael W Lawlor(1)
- Michael A. Rudnicki(4)
- Már Tulinius(1)
- Masahisa Katsuno(1)
- Masad J. Damha(1)
- Linda Pax Lowes(1)
- Louise Rodino-Klapac(1)
- Leanne Ward(1)
- Larry Markham(1)
- Kristy Brown(1)
- Kevin Flanigan(2)
- Kate Bushby(1)
- Karim Wahbi(1)
- Karen Anthony(1)
- Kanneboyina Nagaraju(3)
- Julia M. Hum(1)
- Judith van Deutekom(1)
- Jose I. de las Heras(1)
- Joe Kornegay(1)
- Jin-Hong Shin(1)
- Jessica de Greef(1)
- Jerry R. Mendell(1)
- Jennifer Morgan(1)
- Jack H Vandermeulen(1)
- Hongping Zhang(1)
- Heike Kolbel(2)
- Hanns Lochmuller(2)
- Haluk Topaloglu(1)
- Guillaume Bourque(1)
- George Dickson(1)
- Gary Sweeney(1)
- Frank Rigo(1)
- Francesco Muntoni(2)
- Erik Landfeldt(2)
- Eric P. Hoffman(4)
- Eric C. Schirmer(1)
- En Kimura(1)
- Ehsan Javandoost(2)
- David L Mack(1)
- Davi Mazala(1)
- Craig M McDonald(1)
- Christian Werner(1)
- Capucine Trollet(1)
- Benedikt Schoser(1)
- Arnaud Ferry(1)
- Arezu Jahani-Asl(1)
- Antoni Borrell(1)
- Anthony Scimè(1)
- Annemieke Aartsma-Rus(5)
- Anne Schänzer(2)
- Anastasia Khvorova(1)
- Alyson Fiorillo(3)
- Allison D Ebert(1)
- Alessandra Sacco(1)
- Alastair R.W. Kerr(1)
- Akinori Nakamura(3)
- Terminology(10)
- Tools and Materials(5)
- Useful information(22)
- muscle diseases(6)
- Articles(72)
- DystroBlog | پژوهش و اخبار بیماریهای عصبی-عضلانی(96)
- Matthew S Alexander(1)
- Louis M. Kunkel(1)
- Karyn Esser(1)