more
Introducing JIF Hub: Your All-in-One Journal Impact Factor Tool
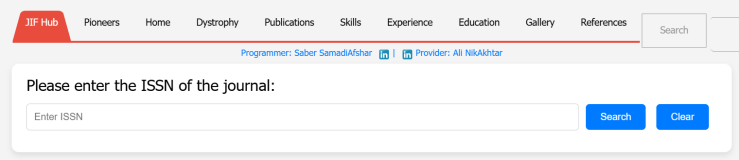
Introducing JIF Hub, a powerful platform for researchers to access Journal Impact Factors (JIF) and key journal metrics. Developed by Saber SamadiAfshar (Afshar Research Group), JIF Hub simplifies journal selection with features like ISSN search, impact factor trends (2020-2023), total citations, quartile rankings, and open-access insights. Designed for researchers, students, and administrators, JIF Hub helps optimize publication decisions and research visibility efficiently.