more
Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of eteplirsen in young boys aged 6–48 months with Duchenne muscular dystrophy amenable to exon 51 skipping

This open-label trial assesses eteplirsen’s safety in young boys with DMD, confirming its tolerability and predictable pharmacokinetics, but further efficacy studies are needed.
more
Mitochondrial Function in Muscle Stem Cell Fates

This study examines mitochondrial function in muscle stem cells, detailing their role in energy metabolism, differentiation, and regeneration under aging and disease conditions.
more
Adrenal Suppression From Vamorolone and Prednisone in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Results From the Phase 2b Clinical Trial

This study examines adrenal suppression in Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients treated with vamorolone and prednisone, emphasizing cortisol thresholds and management strategies.
more
Oligonucleotide Therapies for Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy: Current Preclinical Landscape

This article reviews oligonucleotide-based therapies for facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy, highlighting antisense oligonucleotides, RNAi, and CRISPR-based approaches targeting DUX4.
more
A multistage sequencing strategy pinpoints novel candidate alleles for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy and supports gene misregulation as its pathomechanism

This study utilizes a multistage sequencing strategy to uncover novel candidate alleles for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy and supports gene misregulation as a key pathomechanism.
more
MitoNEET preserves muscle insulin sensitivity during ironoverload by regulating mitochondrial iron, reactive oxygenspecies and fission

Explore how MitoNEET preserves muscle insulin sensitivity during iron overload by regulating mitochondrial iron, ROS levels, and mitochondrial fission.
more
An update on Becker muscular dystrophy

This article provides an update on Becker muscular dystrophy research, highlighting advances in diagnosis, natural history studies, and emerging treatment approaches.
more
High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is a potential disease biomarker in cell and mouse models of Duchenne muscular dystrophy

Explore the role of HMGB1 as a potential biomarker for Duchenne muscular dystrophy, monitoring disease progression and gene therapy efficacy.
more
Prenatal Exome Sequencing Analysis in Fetuses with Various Ultrasound Findings

This study evaluates the role of prenatal exome sequencing in detecting genetic disorders in fetuses with ultrasound findings, comparing its utility to chromosomal microarray analysis.
more
Transcriptional dysregulation of autophagy in the muscle of a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy
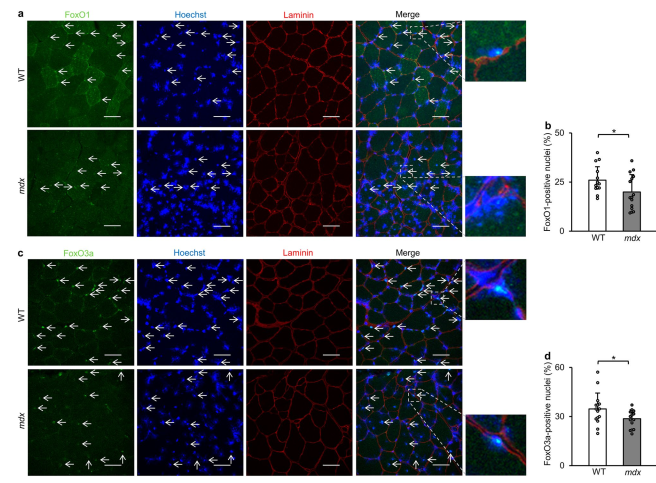
This study explores autophagy dysregulation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy, highlighting FoxO and TFEB inactivation and resveratrol's role in restoring autophagy.
more
REST/NRSF preserves muscle stem cell identity and survival by repressing alternate cell fates

This study explores the role of REST/NRSF in preserving muscle stem cell identity by repressing non-muscle genes, ensuring proper regeneration and self-renewal.
more
Recent Progress in Gene-Targeting Therapies for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Promises and Challenges

This review discusses gene-targeting therapies for spinal muscular atrophy, covering antisense oligonucleotides, gene replacement, small molecules, and treatment challenges.
more
Glucose Metabolism as a Pre-clinical Biomarker for the Golden Retriever Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
This study evaluates glucose metabolism as a biomarker in the GRMD model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, analyzing GLUT4 expression, PET/CT imaging, and metabolic regulation.
more
Impaired Glucose Tolerance in Adults with Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy

Abstract This study aimed to evaluate glucose tolerance in adult males with Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) and Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) using an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). The study investigated whether body composition influences glucose response. Participants: 28 adults with dystrophinopathy (13 BMD, 15 DMD) and 12 non-dystrophic controls. Method: 75g glucose ingestion with fingertip blood sampling every 30 minutes for 2 hours. Results: Higher glucose levels in …
more
Recent Posts
Categories
- DystroBlog | Neuromuscular Disease Research & News(96)
- Christopher W Ward(1)
- Jeffrey Chamberlain(2)
- Douglas Millay(1)
- Luis Garcia(1)
- Vincent Mouly(1)
- Bible(1)
- Yusuke Echigoya(2)
- Yuko Shimizu-Motohashi(1)
- Yu-Chiang Lai(1)
- Ype Elgersma(1)
- Yoshitsugu Aoki(1)
- Yetrib Hathout(1)
- Yasuhiro Yamada(1)
- W. David Arnold(1)
- Volker Straub(3)
- Virginia Arechavala-Gomeza(1)
- Vahab Soleimani(1)
- Utkarsh J. Dang(2)
- Toshifumi Yokota(13)
- Tony Kwan(1)
- Tobias Ruck(3)
- Tim Hagenacker(1)
- Thomas Sejersen(1)
- Theodore Perkins(1)
- Terry Partridge(1)
- Steve Wilton(1)
- Stephen Tapscott(1)
- Silvere van der Maarel(1)
- Shin’ichi Takeda(2)
- Ryszard Kole(1)
- Robert Weiss(1)
- Rob W.J. Collin(1)
- Rita Horvath(2)
- Renato Dulbecco(2)
- Rashmi Kothary(1)
- Rafal Czapiewski(1)
- Pim Pijnappel(1)
- Peter Meinke(1)
- Peter F M Van der Ven(2)
- Paula R. Clemens(2)
- Norio Motohashi(1)
- Muthiah Manoharan(1)
- Michela Guglieri(2)
- Michael W Lawlor(1)
- Michael A. Rudnicki(4)
- Már Tulinius(1)
- Masahisa Katsuno(1)
- Masad J. Damha(1)
- Linda Pax Lowes(1)
- Louise Rodino-Klapac(1)
- Leanne Ward(1)
- Larry Markham(1)
- Kristy Brown(1)
- Kevin Flanigan(2)
- Kate Bushby(1)
- Karim Wahbi(1)
- Karen Anthony(1)
- Kanneboyina Nagaraju(3)
- Julia M. Hum(1)
- Judith van Deutekom(1)
- Jose I. de las Heras(1)
- Joe Kornegay(1)
- Jin-Hong Shin(1)
- Jessica de Greef(1)
- Jerry R. Mendell(1)
- Jennifer Morgan(1)
- Jack H Vandermeulen(1)
- Hongping Zhang(1)
- Heike Kolbel(2)
- Hanns Lochmuller(2)
- Haluk Topaloglu(1)
- Guillaume Bourque(1)
- George Dickson(1)
- Gary Sweeney(1)
- Frank Rigo(1)
- Francesco Muntoni(2)
- Erik Landfeldt(2)
- Eric P. Hoffman(4)
- Eric C. Schirmer(1)
- En Kimura(1)
- Ehsan Javandoost(2)
- David L Mack(1)
- Davi Mazala(1)
- Craig M McDonald(1)
- Christian Werner(1)
- Capucine Trollet(1)
- Benedikt Schoser(1)
- Arnaud Ferry(1)
- Arezu Jahani-Asl(1)
- Antoni Borrell(1)
- Anthony Scimè(1)
- Annemieke Aartsma-Rus(5)
- Anne Schänzer(2)
- Anastasia Khvorova(1)
- Alyson Fiorillo(3)
- Allison D Ebert(1)
- Alessandra Sacco(1)
- Alastair R.W. Kerr(1)
- Akinori Nakamura(3)
- Terminology(10)
- Tools and Materials(5)
- Useful information(22)
- muscle diseases(6)
- Articles(72)
- DystroBlog | پژوهش و اخبار بیماریهای عصبی-عضلانی(96)
- Matthew S Alexander(1)
- Louis M. Kunkel(1)
- Karyn Esser(1)