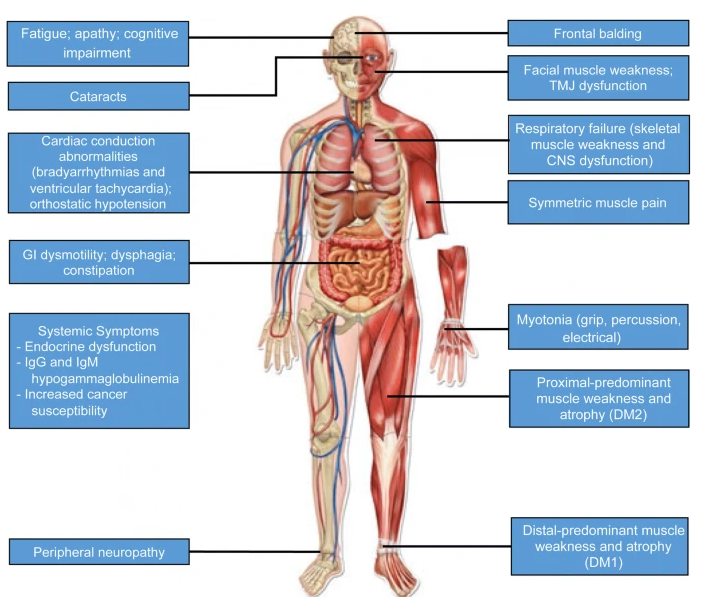
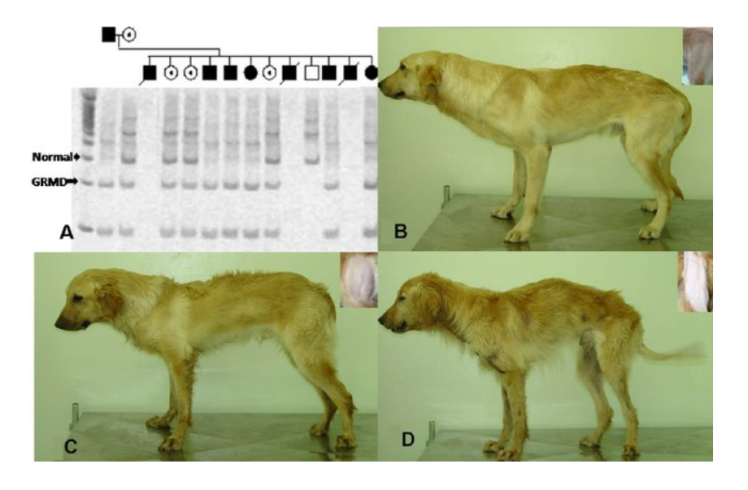
more
Molecular composition of skeletal muscle in infants and adults: a comparative proteomic and transcriptomic study

This paper investigates the molecular differences between infant and adult skeletal muscles using proteomic and transcriptomic approaches. Researchers collected muscle biopsies from infants (aged 4-28 months) and adults (aged 19-65 years) to identify age-related changes. The study found significant differences in the expression of genes and proteins responsible for muscle structure, metabolism, and immune responses between these two groups. In infants, muscle fibers are less mature, and processes related to …